QTL analysis and GWAS of agronomic traits in sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas L.) using genome wide SNPs
- PMID: 32714050
- PMCID: PMC7372034
- DOI: 10.1270/jsbbs.19099
QTL analysis and GWAS of agronomic traits in sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas L.) using genome wide SNPs
Abstract
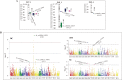
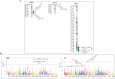
While sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas L.) improvement has generally been done by field-based selection, molecular genetic studies on traits of interest, i.e., molecular markers are needed for enhancing the breeding program of this world's 7th most important crop, as such markers facilitate marker-assisted selection. Here, we performed a combined approach of QTLs analyses and GWAS of storage root β-carotene content (BC), dry-matter (DM) and starch content (SC) using the genetic linkage maps constructed with 5,952 and 5,640 SNPs obtained from F1 progenies between cultivars 'J-Red' and 'Choshu'. BC was negatively correlated with DM (r = -0.45) and SC (r = -0.51), while DM was positively correlated with SC (r = 0.94). In both parental maps, a total of five, two and five QTL regions on linkage groups 7 and 8 were associated with BC, DM and SC, respectively. In GWAS of BC, one strong signal (P = 1.04 × 10-9) was observed on linkage group 8, which co-located with one of the above QTL regions. The SNPs markers found here, particularly for β-carotene, would be useful base resources for future marker-assisted selection program with this trait.
Keywords: GWAS; QTL; ddRAD SNPs; root dry-matter; starch; sweetpotato; β-carotene.
Copyright © 2020 by JAPANESE SOCIETY OF BREEDING.
Figures

References
-
- Beyer P., Al-Babili S., Ye X., Lucca P., Schaub P., Welsch R. and Potrykus I. (2002) Golden rice: introducing the beta-carotene biosynthesis pathway into rice endosperm by genetic engineering to defeat vitamin A deficiency. Symposium: plant breeding: a new tool for fighting micronutrient malnutrition. Am. Soc. Nutrit. Sci. 132: 506S–510S. - PubMed
-
- Brabet, C., D. Reynoso, D. Dufour, C. Mestres, J. Arredondo and G.J. Scott (1998) Starch content and properties of 106 sweetpotato clones from the world germplasm collection held at CIP, Peru. CIP Program Rep. 1997–98: impact on a challenging world. International Potato Center, Lima.
-
- Bradbury P.J., Zhang Z., Kroon D.E., Casstevens T.M., Ramdoss Y. and Buckler E.S. (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23: 2633–2635. - PubMed
-
- Buléon A., Colonna P., Planchot V. and Ball S. (1998) Starch granules: structure and biosynthesis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 23: 85–112. - PubMed
-
- Cervantes-Flores J.C., Yencho G.C., Kriegner A., Pecota K.V., Faulk M.A., Mwanga R.O.M. and Sosinski B.R. (2008) Development of a genetic linkage map and identification of homologous linkage groups in sweetpotato using multiple-dose AFLP markers. Mol. Breed. 21: 511–532.

