GABAergic Inhibitory Interneuron Deficits in Alzheimer's Disease: Implications for Treatment
- PMID: 32714136
- PMCID: PMC7344222
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00660
GABAergic Inhibitory Interneuron Deficits in Alzheimer's Disease: Implications for Treatment
Abstract
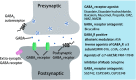
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized clinically by severe cognitive deficits and pathologically by amyloid plaques, neuronal loss, and neurofibrillary tangles. Abnormal amyloid β-protein (Aβ) deposition in the brain is often thought of as a major initiating factor in AD neuropathology. However, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) inhibitory interneurons are resistant to Aβ deposition, and Aβ decreases synaptic glutamatergic transmission to decrease neural network activity. Furthermore, there is now evidence suggesting that neural network activity is aberrantly increased in AD patients and animal models due to functional deficits in and decreased activity of GABA inhibitory interneurons, contributing to cognitive deficits. Here we describe the roles played by excitatory neurons and GABA inhibitory interneurons in Aβ-induced cognitive deficits and how altered GABA interneurons regulate AD neuropathology. We also comprehensively review recent studies on how GABA interneurons and GABA receptors can be exploited for therapeutic benefit. GABA interneurons are an emerging therapeutic target in AD, with further clinical trials urgently warranted.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; GABA inhibitory interneurons; PV inhibitory interneurons; amyloid β-protein; cognitive deficits.
Copyright © 2020 Xu, Zhao, Han and Zhang.
Figures


References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association (2019). Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 15 321–387. 10.1016/j.jalz.2019.01.010 - DOI
-
- Andrews-Zwilling Y., Bien-Ly N., Xu Q., Li G., Bernardo A., Yoon S. Y., et al. (2010). Apolipoprotein E4 causes age- and Tau-dependent impairment of GABAergic interneurons, leading to learning and memory deficits in mice. J. Neurosci. 30 13707–13717. 10.1523/jneurosci.4040-10.2010 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

