Culturing primary neurons from rat hippocampus and cortex
- PMID: 32714598
- PMCID: PMC7363313
- DOI: 10.1042/NS20180207
Culturing primary neurons from rat hippocampus and cortex
Abstract
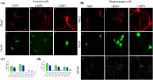
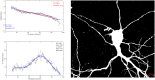
Primary neurons from rodent brain hippocampus and cortex have served as important tools in biomedical research over the years. However, protocols for the preparation of primary neurons vary, which often lead to conflicting results. This report provides a robust and reliable protocol for the production of primary neuronal cultures from the cortex and hippocampus with minimal contribution of non-neuronal cells. The neurons were grown in serum-free media and maintained for several weeks without any additional feeder cells. The neuronal cultures maintained according to this protocol differentiate and by 3 weeks develop extensive axonal and dendritic branching. The cultures produced by this method show excellent reproducibility and can be used for histological, molecular and biochemical methods.
Keywords: cerebral cortex; hippocampus; primary neuron.
© 2019 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

