Candida chorioamnionitis associated with late stillbirth: A case report
- PMID: 32714843
- PMCID: PMC7372140
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crwh.2020.e00239
Candida chorioamnionitis associated with late stillbirth: A case report
Abstract
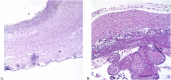
Vulvovaginal candidiasis during pregnancy is common, but serious complications, including chorioamnionitis, are infrequent. A 41-year-old woman presented at 37 weeks of gestation with reduced fetal movements, and fetal death in utero was subsequently confirmed on ultrasound. Histopathology of the cord and placenta revealed Candida infection and microabscesses on the umbilical cord. Overall, these features are suggestive of ascending infection, consistent with Candida as the causative organism. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported case of late stillbirth due to Candida chorioamnionitis. More research is needed to determine the mechanism whereby Candida becomes pathogenic in pregnancy. There is also no clear consensus on how to manage such patients in a subsequent pregnancy.
Keywords: Candida; Case report; Chorioamnionitis; Infection; Stillbirth.
© 2020 The Authors.
Figures
References
-
- Bittencourt A., dos Santos W., de Oliveira C. Placenta and fetal candidiasis - presentation of a case of an abortus. Miycopathologia. 1984;87:181–187. - PubMed
-
- Roque H., Abdelhak Y., Young B.K. Intra amniotic candidiasis. Case report and meta-analysis of 54 cases. J. Perinat. Med. 1999;27(4):253–262. - PubMed
-
- Jackel D., Lai K. Candida glabrata Sepsis associated with chorioamnionitis in an in vitro fertilization pregnancy: case report and review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013;56(4):555–558. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources