Typical imaging finding of hepatic infections: a pictorial essay
- PMID: 32715334
- PMCID: PMC7897188
- DOI: 10.1007/s00261-020-02642-z
Typical imaging finding of hepatic infections: a pictorial essay
Abstract
Hepatic infections are frequent in clinical practice. Although epidemiological, clinical and laboratory data may suggest hepatic infection in certain cases, imaging is nearly always necessary to confirm the diagnosis, assess disease extension and its complications, evaluate the response to treatment, and sometimes to make differential diagnoses such as malignancies. Ultrasound (US) is usually the first-line investigation, while computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) provide better characterization and a more precise assessment of local extension, especially biliary and vascular. The purpose of this article is to describe the typical features and main complications of common hepatic infections. Familiarity with the radiological features of this entity can help suggest the correct diagnosis and the need for further studies as well as determine appropriate and timely treatment.
Keywords: Hepatic infection; Liver imaging; Liver infection.
Figures


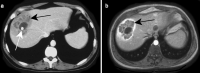
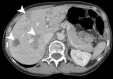
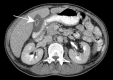
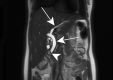
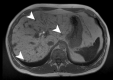
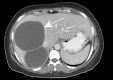
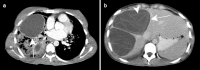
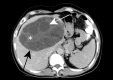
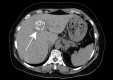
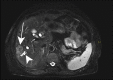
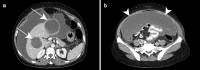

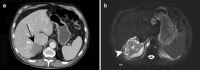

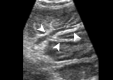

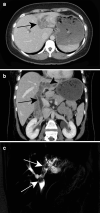

References
-
- Rahimian J, Wilson T, Oram V, Holzman RS (2004) Pyogenic liver abscess: recent trends in etiology and mortality. Clin Infect Dis 39 (11):1654-1659. 10.1086/425616 - PubMed
-
- Seeto RK, Rockey DC (1996) Pyogenic liver abscess. Changes in etiology, management, and outcome. Medicine (Baltimore) 75 (2):99-113. 10.1097/00005792-199603000-00006 - PubMed
-
- Okano H, Shiraki K, Inoue H, Kawakita T, Yamamoto N, Deguchi M, Sugimoto K, Sakai T, Ohmori S, Murata K, Nakano T (2002) Clinicopathological analysis of liver abscess in Japan. Int J Mol Med 10 (5):627-630 - PubMed
-
- Siu LK, Yeh KM, Lin JC, Fung CP, Chang FY (2012) Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess: a new invasive syndrome. Lancet Infect Dis 12 (11):881-887. 10.1016/s1473-3099(12)70205-0 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

