Distal convoluted tubule Cl- concentration is modulated via K+ channels and transporters
- PMID: 32715757
- PMCID: PMC7509289
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00284.2020
Distal convoluted tubule Cl- concentration is modulated via K+ channels and transporters
Abstract
Cl--sensitive with-no-lysine kinase (WNK) plays a key role in regulating the thiazide-sensitive Na+-Cl- cotransporter (NCC) in the distal convoluted tubule (DCT). Cl- enters DCT cells through NCC and leaves the cell across the basolateral membrane via the Cl- channel ClC-K2 or K+-Cl- cotransporter (KCC). While KCC is electroneutral, Cl- exit via ClC-K2 is electrogenic. Therefore, an alteration in DCT basolateral K+ channel activity is expected to influence Cl- movement across the basolateral membrane. Although a role for intracellular Cl- in the regulation of WNK and NCC has been established, intracellular Cl- concentrations ([Cl-]i) have not been directly measured in the mammalian DCT. Therefore, to measure [Cl-]i in DCT cells, we generated a transgenic mouse model expressing an optogenetic kidney-specific Cl-Sensor and measured Cl- fluorescent imaging in the isolated DCT. Basal measurements indicated that the mean [Cl-]i was ~7 mM. Stimulation of Cl- exit with low-Cl- hypotonic solutions decreased [Cl-]i, whereas inhibition of KCC by DIOA or inhibition of ClC-K2 by NPPB increased [Cl-]i, suggesting roles for both KCC and ClC-K2 in the modulation of [Cl-]i . Blockade of basolateral K+ channels (Kir4.1/5.1) with barium significantly increased [Cl-]i. Finally, a decrease in extracellular K+ concentration transiently decreased [Cl-]i, whereas raising extracellular K+ transiently increased [Cl-]i, further suggesting a role for Kir4.1/5.1 in the regulation of [Cl-]i. We conclude that the alteration in ClC-K2, KCC, and Kir4.1/5.1 activity influences [Cl-]i in the DCT.
Keywords: K+-Cl− cotransporter; Na+-Cl− cotransporter; chloride; chloride channel; potassium channel.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the author(s).
Figures
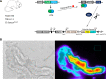
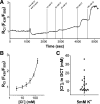


References
-
- Bazúa-Valenti S, Chávez-Canales M, Rojas-Vega L, González-Rodríguez X, Vázquez N, Rodríguez-Gama A, Argaiz ER, Melo Z, Plata C, Ellison DH, García-Valdés J, Hadchouel J, Gamba G. The effect of WNK4 on the Na+-Cl− cotransporter is modulated by intracellular chloride. J Am Soc Nephrol 26: 1781–1786, 2015. doi:10.1681/ASN.2014050470. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boettger T, Rust MB, Maier H, Seidenbecher T, Schweizer M, Keating DJ, Faulhaber J, Ehmke H, Pfeffer C, Scheel O, Lemcke B, Horst J, Leuwer R, Pape HC, Völkl H, Hübner CA, Jentsch TJ. Loss of K-Cl co-transporter KCC3 causes deafness, neurodegeneration and reduced seizure threshold. EMBO J 22: 5422–5434, 2003. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg519. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

