Dissecting transcriptional amplification by MYC
- PMID: 32715994
- PMCID: PMC7384857
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.52483
Dissecting transcriptional amplification by MYC
Abstract
Supraphysiological MYC levels are oncogenic. Originally considered a typical transcription factor recruited to E-boxes (CACGTG), another theory posits MYC a global amplifier increasing output at all active promoters. Both models rest on large-scale genome-wide "-omics'. Because the assumptions, statistical parameter and model choice dictates the '-omic' results, whether MYC is a general or specific transcription factor remains controversial. Therefore, an orthogonal series of experiments interrogated MYC's effect on the expression of synthetic reporters. Dose-dependently, MYC increased output at minimal promoters with or without an E-box. Driving minimal promoters with exogenous (glucocorticoid receptor) or synthetic transcription factors made expression more MYC-responsive, effectively increasing MYC-amplifier gain. Mutations of conserved MYC-Box regions I and II impaired amplification, whereas MYC-box III mutations delivered higher reporter output indicating that MBIII limits over-amplification. Kinetic theory and experiments indicate that MYC activates at least two steps in the transcription-cycle to explain the non-linear amplification of transcription that is essential for global, supraphysiological transcription in cancer.
Keywords: MYC; cancer; cancer biology; computational biology; general amplifier; human; kinetic mechanism of action; michaelis-menten kinetics; systems biology; transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
ZN, CG, SD, CC, EB, SS, DL No competing interests declared
Figures



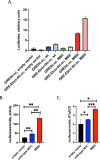
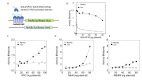
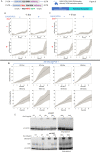
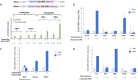
References
-
- Alon U. An Introduction to Systems Biology : Design Principles of Biological Circuits. Chapman & Hall/CRC; 2007.
-
- Baluapuri A, Hofstetter J, Dudvarski Stankovic N, Endres T, Bhandare P, Vos SM, Adhikari B, Schwarz JD, Narain A, Vogt M, Wang SY, Düster R, Jung LA, Vanselow JT, Wiegering A, Geyer M, Maric HM, Gallant P, Walz S, Schlosser A, Cramer P, Eilers M, Wolf E. MYC recruits SPT5 to RNA polymerase II to promote processive transcription elongation. Molecular Cell. 2019;74:674–687. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.02.031. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blackford JA, Guo C, Zhu R, Dougherty EJ, Chow CC, Simons SS. Identification of location and kinetically defined mechanism of cofactors and reporter genes in the cascade of steroid-regulated transactivation. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2012;287:40982–40995. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.414805. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

