Molecular Basis of Atrial Fibrillation Pathophysiology and Therapy: A Translational Perspective
- PMID: 32717172
- PMCID: PMC7398486
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316363
Molecular Basis of Atrial Fibrillation Pathophysiology and Therapy: A Translational Perspective
Abstract
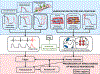
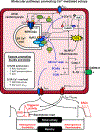
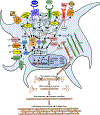
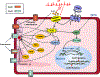
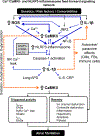
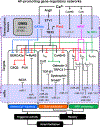
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a highly prevalent arrhythmia, with substantial associated morbidity and mortality. There have been significant management advances over the past 2 decades, but the burden of the disease continues to increase and there is certainly plenty of room for improvement in treatment options. A potential key to therapeutic innovation is a better understanding of underlying fundamental mechanisms. This article reviews recent advances in understanding the molecular basis for AF, with a particular emphasis on relating these new insights to opportunities for clinical translation. We first review the evidence relating basic electrophysiological mechanisms to the characteristics of clinical AF. We then discuss the molecular control of factors leading to some of the principal determinants, including abnormalities in impulse conduction (such as tissue fibrosis and other extra-cardiomyocyte alterations, connexin dysregulation and Na+-channel dysfunction), electrical refractoriness, and impulse generation. We then consider the molecular drivers of AF progression, including a range of Ca2+-dependent intracellular processes, microRNA changes, and inflammatory signaling. The concept of key interactome-related nodal points is then evaluated, dealing with systems like those associated with CaMKII (Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase-II), NLRP3 (NACHT, LRR, and PYD domains-containing protein-3), and transcription-factors like TBX5 and PitX2c. We conclude with a critical discussion of therapeutic implications, knowledge gaps and future directions, dealing with such aspects as drug repurposing, biologicals, multispecific drugs, the targeting of cardiomyocyte inflammatory signaling and potential considerations in intervening at the level of interactomes and gene-regulation. The area of molecular intervention for AF management presents exciting new opportunities, along with substantial challenges.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; calcium; inflammasome; myocytes, cardiac; transcription factors.
Figures

References
-
- Andrade J, Khairy P, Dobrev D, Nattel S. The clinical profile and pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation: relationships among clinical features, epidemiology, and mechanisms. Circ Res. 2014;114:1453–1468 - PubMed
-
- Nattel S, Guasch E, Savelieva I, et al. Early management of atrial fibrillation to prevent cardiovascular complications. Eur Heart J. 2014;35:1448–1456 - PubMed
-
- Lau DH, Nattel S, Kalman JM, Sanders P. Modifiable Risk Factors and Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation. 2017;136:583–596 - PubMed
-
- Wijffels MC, Kirchhof CJ, Dorland R, Allessie MA. Atrial fibrillation begets atrial fibrillation. A study in awake chronically instrumented goats. Circulation. 1995;92:1954–1968 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

