Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Osteosarcoma: From Mechanisms to Therapy
- PMID: 32717819
- PMCID: PMC7432207
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21155207
Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Osteosarcoma: From Mechanisms to Therapy
Abstract
Osteosarcomas (OSs) are bone tumors most commonly found in pediatric and adolescent patients characterized by high risk of metastatic progression and recurrence after therapy. Effective therapeutic management of this disease still remains elusive as evidenced by poor patient survival rates. To achieve a more effective therapeutic management regimen, and hence patient survival, there is a need to identify more focused targeted therapies for OSs treatment in the clinical setting. The role of the OS tumor stroma microenvironment plays a significant part in the development and dissemination of this disease. Important components, and hence potential targets for treatment, are the tumor-infiltrating macrophages that are known to orchestrate many aspects of OS stromal signaling and disease progression. In particular, increased infiltration of M2-like tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) has been associated with OS metastasis and poor patient prognosis despite currently used aggressive therapies regimens. This review aims to provide a summary update of current macrophage-centered knowledge and to discuss the possible roles that macrophages play in the process of OS metastasis development focusing on the potential influence of stromal cross-talk signaling between TAMs, cancer-stem cells and additional OSs tumoral microenvironment factors.
Keywords: cancer-stem cells; mesenchymal stem cells; metastasis; osteosarcomas (OSs); therapy; tumor microenvironment; tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
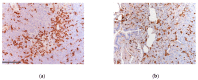

References
-
- Zhang B., Zhang Y., Li R., Li J., Lu X., Zhang Y. The efficacy and safety comparison of first-line chemotherapeutic agents (high-dose methotrexate, doxorubicin, cisplatin, and ifosfamide) for osteosarcoma: A network meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020;15:51. doi: 10.1186/s13018-020-1576-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buddingh E.P., Kuijjer M.L., Duim R.A., Bürger H., Agelopoulos K., Myklebost O., Serra M., Mertens F., Hogendoorn P.C., Lankester A.C., et al. Tumor-infiltrating macrophages are associated with metastasis suppression in high-grade osteosarcoma: A rationale for treatment with macrophage activating agents. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011;17:2110–2119. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2047. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Han Y., Guo W., Ren T., Huang Y., Wang S., Liu K., Zheng B., Yang K., Zhang H., Liang X. Tumor-associated macrophages promote lung metastasis and induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition in osteosarcoma by activating the COX-2/STAT3 axis. Cancer Lett. 2019;440–441:116–125. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.10.011. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

