Functions of Bacterial tRNA Modifications: From Ubiquity to Diversity
- PMID: 32718697
- PMCID: PMC8865055
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tim.2020.06.010
Functions of Bacterial tRNA Modifications: From Ubiquity to Diversity
Abstract
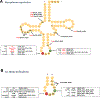
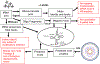
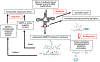
Modified nucleotides in tRNA are critical components of the translation apparatus, but their importance in the process of translational regulation had until recently been greatly overlooked. Two breakthroughs have recently allowed a fuller understanding of the importance of tRNA modifications in bacterial physiology. One is the identification of the full set of tRNA modification genes in model organisms such as Escherichia coli K12. The second is the improvement of available analytical tools to monitor tRNA modification patterns. The role of tRNA modifications varies greatly with the specific modification within a given tRNA and with the organism studied. The absence of these modifications or reductions can lead to cell death or pleiotropic phenotypes or may have no apparent visible effect. By linking translation through their decoding functions to metabolism through their biosynthetic pathways, tRNA modifications are emerging as important components of the bacterial regulatory toolbox.
Keywords: decoding efficiency; post-transcriptional regulation; translation.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- El Yacoubi B et al. (2012) Biosynthesis and function of posttranscriptional modifications of Transfer RNAs. Annu. Rev. Genet 46, 69–95 - PubMed
-
- Grosjean H et al. (2010) Deciphering synonymous codons in the three domains of life: Co-evolution with specific tRNA modification enzymes. FEBS Lett. 584, 252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

