Isolating live cell clones from barcoded populations using CRISPRa-inducible reporters
- PMID: 32719478
- PMCID: PMC7616981
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-020-0614-0
Isolating live cell clones from barcoded populations using CRISPRa-inducible reporters
Abstract
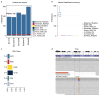
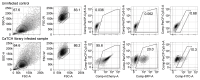
We developed a functional lineage tracing tool termed CaTCH (CRISPRa tracing of clones in heterogeneous cell populations). CaTCH combines precise clonal tracing of millions of cells with the ability to retrospectively isolate founding clones alive before and during selection, allowing functional experiments. Using CaTCH, we captured rare clones representing as little as 0.001% of a population and investigated the emergence of resistance to targeted melanoma therapy in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures










References
-
- Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF, Weissman IL. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature. 2001;414:105–111. - PubMed
-
- Simons BD, Clevers H. Strategies for Homeostatic Stem Cell Self-Renewal in Adult Tissues. Cell. 2011;145:851–862. - PubMed
-
- Shakiba N, et al. Cell competition during reprogramming gives rise to dominant clones. Science (80-) 2019;364:eaan0925. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

