Classification of T-cell activation via autofluorescence lifetime imaging
- PMID: 32719514
- PMCID: PMC7854821
- DOI: 10.1038/s41551-020-0592-z
Classification of T-cell activation via autofluorescence lifetime imaging
Abstract
The function of a T cell depends on its subtype and activation state. Here, we show that imaging of the autofluorescence lifetime signals of quiescent and activated T cells can be used to classify the cells. T cells isolated from human peripheral blood and activated in culture using tetrameric antibodies against the surface ligands CD2, CD3 and CD28 showed specific activation-state-dependent patterns of autofluorescence lifetime. Logistic regression models and random forest models classified T cells according to activation state with 97-99% accuracy, and according to activation state (quiescent or activated) and subtype (CD3+CD8+ or CD3+CD4+) with 97% accuracy. Autofluorescence lifetime imaging can be used to non-destructively determine T-cell function.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
A.W. and M.S. are mentioned as co-inventors in a patent application (“Systems and methods for sorting T cells by activation state”, #62/724428, August 2018) covering devices and methods to sort T cells based on fluorescence-lifetime components.
Figures

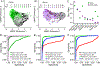
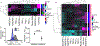
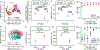
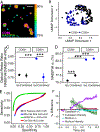
Comment in
-
Label-free T cell characterization.Nat Methods. 2020 Oct;17(10):957. doi: 10.1038/s41592-020-00975-7. Nat Methods. 2020. PMID: 32994563 No abstract available.
References
-
- Mosmann TR & Coffman RL in Advances in Immunology Volume 46 111–147 (Elsevier, 1989). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

