Upper Extremity Compressive Neuropathies in the Pediatric and Adolescent Populations
- PMID: 32720100
- PMCID: PMC7661676
- DOI: 10.1007/s12178-020-09666-4
Upper Extremity Compressive Neuropathies in the Pediatric and Adolescent Populations
Abstract
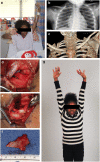
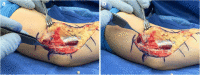
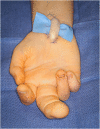
Purpose of review: Although somewhat rare, upper extremity compressive neuropathies can occur in the pediatric and adolescent populations due to various etiologies. Some of the most common conditions seen include thoracic outlet syndrome, supracondylar process syndrome, cubital tunnel syndrome with subluxation of the ulnar nerve, and carpal tunnel syndrome. This review will focus on these diagnoses and how to address them in the pediatric and adolescent populations.
Recent findings: Due to the rarity of upper extremity compressive neuropathies in the pediatric and adolescent populations, substantial advancement in the literature does not routinely occur. However, recent literature has found a difference in the rate of various subtypes of thoracic outlet syndrome in children versus adults. Additionally, cubital tunnel syndrome associated with ulnar nerve subluxation/instability has recently been found to have better outcomes following surgical decompression of the ulnar nerve and transposition than those with stable ulnar nerves. In summary, this review provides the most recent knowledge surrounding upper extremity compressive and entrapment neuropathies in the pediatric and adolescent populations.
Keywords: Carpal tunnel syndrome; Cubital tunnel syndrome; Lipofibromatous hamartoma; Mucopolysaccharidoses; Supracondylar process; Thoracic outlet syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
Casey M. Codd and Joshua M. Abzug declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Roos DB. Overview of thoracic outlet syndromes. In: Machleder HI, editor. Vascular disorders of the upper extremity. Mount Kisco, NY: Futura; 1989. pp. 155–177.
-
- •• Ransom EF, Minton HL, Young BL, He JK, Ponce BA, McGwin G, Meyer RD, Brabston EW 3rd. Intermediate and long-term outcomes following surgical decompression of neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome in an adolescent patient population. Hand (N.Y.). 2020 [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1177/1558944719901. Outcomes following surgical intervention for neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome in a large pediatric and adolescent cohort, both short and long term, were noted to be favorable in relieving symptoms. No statistical difference was found in quantitative measures between pre- and post-operative VAS and SANE scores. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

