Sleeping trees and sleep-related behaviours of the siamang (Symphalangus syndactylus) in a tropical lowland rainforest, Sumatra, Indonesia
- PMID: 32720108
- PMCID: PMC7813730
- DOI: 10.1007/s10329-020-00849-8
Sleeping trees and sleep-related behaviours of the siamang (Symphalangus syndactylus) in a tropical lowland rainforest, Sumatra, Indonesia
Abstract
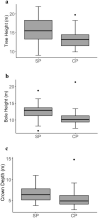
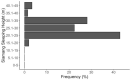
Sleeping tree selection and related behaviours of a family group and a solitary female siamang (Symphalangus syndactylus) were investigated over a 5-month period in northern Sumatra, Indonesia. We performed all day follows, sleeping tree surveys and forest plot enumerations in the field. We tested whether: (1) physical characteristics of sleeping trees and the surrounding trees, together with siamang behaviours, supported selection based on predation risk and access requirements; (2) the preferences of a solitary siamang were similar to those of a family group; and (3) sleeping site locations within home ranges were indicative of home range defence, scramble competition with other groups or other species, or food requirements. Our data showed that (1) sleeping trees were tall, emergent trees with some, albeit low, connectivity to the neighbouring canopy, and that they were surrounded by other tall trees. Siamangs showed early entry into and departure from sleeping trees, and slept at the ends of branches. These results indicate that the siamangs' choice of sleeping trees and related behaviours were strongly driven by predator avoidance. The observed regular reuse of sleeping sites, however, did not support anti-predation theory. (2) The solitary female displayed selection criteria for sleeping trees that were similar to those of the family group, but she slept more frequently in smaller trees than the latter. (3) Siamangs selected sleeping trees to avoid neighbouring groups, monopolise resources (competition), and to be near their last feeding tree. Our findings indicate selectivity in the siamangs' use of sleeping trees, with only a few trees in the study site being used for this purpose. Any reduction in the availability of such trees might make otherwise suitable habitat unsuitable for these highly arboreal small apes.
Keywords: Gunung Leuser National Park; Hylobatidae; Leuser Ecosystem; Predation; Primate.
Figures



References
-
- Aldrich-Blake FP, Chivers DJ. On the genesis of a group of siamang. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1973;38:631–636. - PubMed
-
- Alexander C, Korstjens AH, Hankinson E, Usher G, Harrison N, Nowak MG, Abdullah A, Wich SA, Hill RA. Locating emergent trees in a tropical rainforest using data from an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) Int J Appl Earth Obs. 2018;72:86–90.
-
- Anderson JR. Ethology and ecology of sleep in monkeys and apes. Adv Stud Behav. 1984;14:165–229.
-
- Anderson JR. Sleep, sleeping sites, and sleep-related activities: awakening to their significance. Am J Primatol. 1998;46:63–75. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JR. Sleep-related behavioural adaptations in free-ranging anthropoid primates. Sleep Med Rev. 2000;4:355–373. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

