The Effectiveness of a Community-Based Mentoring Program for Children Aged 5-11 Years: Results from a Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 32720189
- PMCID: PMC7762747
- DOI: 10.1007/s11121-020-01132-4
The Effectiveness of a Community-Based Mentoring Program for Children Aged 5-11 Years: Results from a Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
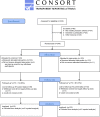
The study, a two-arm, randomized controlled, parallel group, superiority trial, aimed to evaluate the implementation and effectiveness of a 12-month one-to-one volunteer mentoring program designed to improve behavioral and emotional outcomes in children aged 5 to 11 years who have teacher- and parent/carer-reported behavioral difficulties. Participants were 246 children (123 intervention, 123 control; mean age 8.4 years; 87% boys) in five sites in London, UK, scoring in the "abnormal" range on the teacher-rated Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ) Total Difficulties measure and in the "borderline" or abnormal range on the parent-rated SDQ Total Difficulties measure. Randomization on a 1:1 ratio took place using a computer-generated sequence and stratifying by site. Data collectors and statisticians were blind to participant allocation status. Outcome measures focused on parent- and teacher-rated child behavior and emotions, and child-rated self-perception and hope. Intention-to-treat analysis on all 246 randomized participants (using imputed data where necessary) showed that at post-intervention (16 months after randomization), there were no statistically significant effects on the primary outcome-parent-rated SDQ Total Difficulties (adjusted standardized mean difference = - 0.12; 95% CI: -0.38 to 0.13; p = 0.33)-or any secondary outcomes. Results from complier average causal effect (CACE) analysis using the primary outcome indicated the intervention was not effective for children who received the recommended duration of mentoring. Exploratory analyses found no sub-group effects on the primary outcome. The article concludes that the mentoring program had no effect on children's behavior or emotional well-being, and that program content needs revising to satisfactorily address key risk and protective factors.
Keywords: Behavioral and emotional problems; Early intervention; Effectiveness research; Mentoring; Randomized controlled trial.
Conflict of interest statement
Following trial completion, NA worked with Chance UK to adapt the intervention. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Beck AT, Beck RW. Screening depressed patients in family practice. Postgraduate Medicine. 1972;52:81–85. - PubMed
-
- Bond C, Woods K, Humphrey N, Symes W, Green L. The effectiveness of solution focused brief therapy with children and families: A systematic and critical evaluation of the literature from 1990–2010. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry. 2013;54:707–723. - PubMed
-
- Bywater TJ. Perspectives on the Incredible Years programme: Psychological management of conduct disorder. British Journal of Psychiatry. 2012;201:85–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources