Using Digital Communication Technology to Increase HIV Testing Among Men Who Have Sex With Men and Transgender Women: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 32720902
- PMCID: PMC7420634
- DOI: 10.2196/14230
Using Digital Communication Technology to Increase HIV Testing Among Men Who Have Sex With Men and Transgender Women: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: HIV continues to disproportionately affect men who have sex with men (MSM) and transgender women (TW). Undiagnosed HIV is a major driver of HIV transmission rates, and increasing the uptake of regular HIV testing and facilitating timely initiation of HIV treatment is a global HIV prevention priority. However, MSM and TW experience a range of barriers that limit their access to testing and other prevention services. Given their growing ubiquity, digital communication technologies are increasingly being used to support HIV prevention efforts, and a growing number of studies have trialed the use of digital technology to promote HIV testing among MSM and TW.
Objective: We undertook a systematic review and meta-analysis to assess the impact of digital communication technology on HIV testing uptake among MSM and TW. Subanalyses aimed to identify the features and characteristics of digital interventions associated with greater impact.
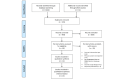
Methods: A systematic literature review was undertaken using select databases and conference repositories. Studies describing the use of a digital technology-internet-enabled devices, including phones, tablets, and computers-to increase HIV testing uptake among MSM or TW using either randomized or observational cohort design with measurement of HIV testing rates measured pre- and postintervention, and published in English between 2010 and 2018 were included. Pooled effect estimates were calculated using a random effects meta-analysis. Subanalyses calculated effect estimates grouped by selected features of digital interventions.
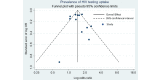
Results: A total of 13 randomized or observational studies were included in the final review. Digital interventions most commonly used mainstream, existing social media platforms (n=7) or promotion through online peer educators (n=5). Most interventions (n=8) were categorized as interactive and allowed user engagement and most directly facilitated testing (n=7) either by providing self-testing kits or referral to testing services. A total of 1930 participants were included across the 13 studies. HIV testing uptake among MSM and TW exposed to digital interventions was 1.5 times higher than that of unexposed MSM and TW (risk ratio [RR] 1.5; 95% CI 1.3-1.7). Subanalyses suggested an increased impact on HIV testing uptake among interventions that were delivered through mainstream social media-based platforms (RR 1.7; 95% CI 1.3-2.1), included direct facilitation of HIV testing (RR 1.6; 95% CI 1.4-1.9), were interactive (RR 1.6; 95% CI 1.4-1.8), and involved end users in the design process (RR 1.6; 95% CI 1.3-2.0).
Conclusions: These findings provide broad support for the integration of technology with existing approaches to promote and facilitate HIV testing among MSM and TW. Our findings identified key features that may be associated with greater impact on HIV testing uptake and can be used to inform future development efforts given the growing interest and application of digital technologies in HIV prevention.
Trial registration: PROSPERO International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews CRD42017070055; https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42017070055.
Keywords: HIV prevention; HIV testing; digital technology; men who have sex with men; transgender women.
©Vanessa Veronese, Kathleen Elizabeth Ryan, Chad Hughes, Megan SC Lim, Alisa Pedrana, Mark Stoové. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (http://www.jmir.org), 28.07.2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
"We are not gays… don't tell me those things": engaging 'hidden' men who have sex with men and transgender women in HIV prevention in Myanmar.BMC Public Health. 2019 Jan 14;19(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-6351-3. BMC Public Health. 2019. PMID: 30642303 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of the effectiveness of respondent-driven and venue-based sampling for identifying undiagnosed HIV infection among cisgender men who have sex with men and transgender women in Tijuana, Mexico.J Int AIDS Soc. 2021 Mar;24(3):e25688. doi: 10.1002/jia2.25688. J Int AIDS Soc. 2021. PMID: 33759361 Free PMC article.
-
Stigma and Web-Based Sex Seeking Among Men Who Have Sex With Men and Transgender Women in Tijuana, Mexico: Cross-Sectional Study.JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2020 Jan 30;6(1):e14803. doi: 10.2196/14803. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2020. PMID: 32031963 Free PMC article.
-
Demand creation and retention strategies for oral pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention among men who have sex with men and transgender women: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Nov 14;23(1):793. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08693-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37964202 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies to increase HIV testing among men who have sex with men and transgender women: an integrative review.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Apr 18;23(1):240. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08124-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37072705 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Potential of HIV Self-Sampling to Increase Testing Frequency Among Gay, Bisexual, and Other Men Who Have Sex With Men, and the Role of Online Result Communication: Online Cross-Sectional Study.J Med Internet Res. 2020 Nov 30;22(11):e21268. doi: 10.2196/21268. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 33252346 Free PMC article.
-
Scaling up delivery of HIV services in Africa through harnessing trends across global emerging innovations.Front Health Serv. 2023 Oct 31;3:1198008. doi: 10.3389/frhs.2023.1198008. eCollection 2023. Front Health Serv. 2023. PMID: 38028944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIV self-testing with digital supports as the new paradigm: A systematic review of global evidence (2010-2021).EClinicalMedicine. 2021 Aug 13;39:101059. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101059. eCollection 2021 Sep. EClinicalMedicine. 2021. PMID: 34430835 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and validation of an information portal on combined HIV prevention.Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2025 May 2;33:e4509. doi: 10.1590/1518-8345.7221.4509. eCollection 2025. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2025. PMID: 40332193 Free PMC article.
-
Peer support to improve the secondary distribution of Internet-based HIV self-testing kits among men who have sex with men in Zhuhai, China.Front Public Health. 2025 Apr 29;13:1522425. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1522425. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40365428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beyrer C, Baral SD, van Griensven F, Goodreau SM, Chariyalertsak S, Wirtz AL, Brookmeyer R. Global epidemiology of HIV infection in men who have sex with men. Lancet. 2012 Jul 28;380(9839):367–77. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60821-6. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/22819660 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baral S, Sifakis F, Cleghorn F, Beyrer C. Elevated risk for HIV infection among men who have sex with men in low- and middle-income countries 2000-2006: a systematic review. PLoS Med. 2007 Dec;4(12):e339. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040339. http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0040339 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Global AIDS Update. UNAIDS. 2016. [2020-06-02]. https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/global-AIDS-updat....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

