Effects of Weight Loss on Obstructive Sleep Apnea Severity. Ten-Year Results of the Sleep AHEAD Study
- PMID: 32721163
- PMCID: PMC7874414
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201912-2511OC
Effects of Weight Loss on Obstructive Sleep Apnea Severity. Ten-Year Results of the Sleep AHEAD Study
Abstract
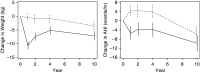
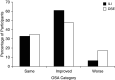
Rationale: Weight loss is recommended to treat obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).Objectives: To determine whether the initial benefit of intensive lifestyle intervention (ILI) for weight loss on OSA severity is maintained at 10 years.Methods: Ten-year follow-up polysomnograms of 134 of 264 adults in Sleep AHEAD (Action for Health in Diabetes) with overweight/obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and OSA were randomized to ILI for weight loss or diabetes support and education (DSE).Measurements and Main Results: Change in apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) was measured. Mean ± SE weight losses of ILI participants of 10.7 ± 0.7, 7.4 ± 0.7, 5.1 ± 0.7, and 7.1 ± 0.8 kg at 1, 2, 4, and 10 years, respectively, were significantly greater than the 1-kg weight loss at 1, 2, and 4 years and 3.5 ± 0.8 kg weight loss at 10 years for the DSE group (P values ≤ 0.0001). AHI was lower with ILI than DSE by 9.7, 8.0, and 7.9 events/h at 1, 2, and 4 years, respectively (P values ≤ 0.0004), and 4.0 events/h at 10 years (P = 0.109). Change in AHI over time was related to amount of weight loss, baseline AHI, visit year (P values < 0.0001), and intervention independent of weight change (P = 0.01). OSA remission at 10 years was more common with ILI (34.4%) than DSE (22.2%).Conclusions: Participants with OSA and type 2 diabetes mellitus receiving ILI for weight loss had reduced OSA severity at 10 years. No difference in OSA severity was present between ILI and DSE groups at 10 years. Improvement in OSA severity over the 10-year period with ILI was related to change in body weight, baseline AHI, and intervention independent of weight change.
Keywords: apnea–hypopnea index; obstructive sleep apnea; lifestyle modification; polysomnogram.
Figures
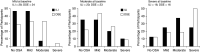
Comment in
-
Weight Loss Is Integral to Obstructive Sleep Apnea Management. Ten-Year Follow-up in Sleep AHEAD.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021 Jan 15;203(2):161-162. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202007-2906ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 32795248 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Young T, Peppard PE, Gottlieb DJ. Epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea: a population health perspective. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165:1217–1239. - PubMed
-
- Gottlieb DJ, Punjabi NM. Diagnosis and management of obstructive sleep apnea: a review. JAMA. 2020;323:1389–1400. - PubMed
-
- Ng SSS, Chan RSM, Woo J, Chan TO, Cheung BHK, Sea MMM, et al. A randomized controlled study to examine the effect of a lifestyle modification program in OSA. Chest. 2015;148:1193–1203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

