COVID-19 induced liver function abnormality associates with age
- PMID: 32721928
- PMCID: PMC7425469
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.103720
COVID-19 induced liver function abnormality associates with age
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a novel infectious disease that may cause fever, dry cough, fatigue and shortness of breath. The impact of COVID-19 on liver function is not well described.
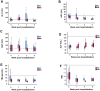
Results: We found that the overall frequency of LFT abnormality was 17.6%. Frequency of LFT abnormality was significantly greater in patients with severe/critical (SC) COVID-19 compared to those with mild/moderate (MM) COVID-19 (32.4% vs 11.6%, p=0.011). Among patients with LFT abnormality, the median age was significantly higher in the SC group compared to the MM group (52 vs 39 years, p=0.021).
Conclusion: COVID-19 is frequently associated with mild liver function abnormality, particularly in individuals with severe/critical COVID-19 who were older. Liver function should be monitored carefully during infection, with judicious use of hepatotoxic agents where possible and avoidance of prolonged hypotension to minimize liver injury in older patients.
Methods: The No. 2 People's Hospital of Fuyang City in China has admitted a total of 159 patients with confirmed COVID-19 since the outbreak from January 2020 to March 2020. We analyzed the incidence of liver function test (LFT) abnormality in these patients with confirmed COVID-19 infection.
Keywords: COVID-19; age; critical patient; liver abnormality; severe.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X, Qu J, Gong F, Han Y, Qiu Y, Wang J, Liu Y, Wei Y, Xia J, Yu T, Zhang X, Zhang L. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet. 2020; 395:507–13. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Menachery VD, Schäfer A, Burnum-Johnson KE, Mitchell HD, Eisfeld AJ, Walters KB, Nicora CD, Purvine SO, Casey CP, Monroe ME, Weitz KK, Stratton KG, Webb-Robertson BM, et al.. MERS-CoV and H5N1 influenza virus antagonize antigen presentation by altering the epigenetic landscape. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018; 115:E1012–21. 10.1073/pnas.1706928115 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

