MTHFR Gene Polymorphisms Prevalence and Cardiovascular Risk Factors Involved in Cardioembolic Stroke Type and Severity
- PMID: 32722170
- PMCID: PMC7463445
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci10080476
MTHFR Gene Polymorphisms Prevalence and Cardiovascular Risk Factors Involved in Cardioembolic Stroke Type and Severity
Abstract
Background: Cardioembolic stroke (CES), generally known as the most severe subtype of ischemic stroke, is related to many factors, including diabetes mellitus (DM), hypertension (HTN), smoking, hyperlipidemia and atrial fibrillation (AF). Genetic mutations of the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene C677T and A1298C have been recently associated with ischemic stroke. The purpose of this study was to analyze the prevalence of MTHFR gene polymorphisms correlated with cardiovascular risk factors in a selected population of patients with CES due to non-valvular AF (NVAF).
Methods: This cross-sectional study was performed on 67 consecutive patients with acute cardioembolic stroke admitted to our hospital. The protocol included general physical examination, neurological clinical status and stroke severity evaluation, imagistic evaluation and genetic testing of MTHFRC677T and A1298C polymorphisms.
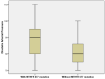
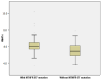
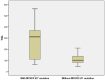
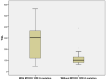
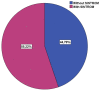
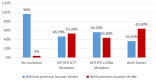
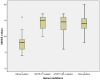
Results: The prevalence of MTHFR polymorphisms in the study population was 38.2% for C677T and 40.3% for A1298C. The C677T mutation was significantly correlated with increased diastolic blood pressure (DBP) values (p = 0.007), higher total cholesterol (TC) (p = 0.003), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDLc) (p = 0.003) and triglycerides (TGL) (p = 0.001), increased high-sensitive C-reactive protein (hsCRP) values (p = 0.015), HbA1c (p = 0.004) and left ventricle ejection fraction (LVEF) (p = 0.047) and lower high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDLc) (p < 0.001) compared to patients without this genetic variant. This genetic profile also included significantly higher CHA2DS2VASC (p = 0.029) and HASBLED (Hypertension, Abnormal liver/renal function, Stroke, Bleeding, Labile INR, Elderly age(>65 years), Drug/Alcohol usage history/Medication usage with bleeding predisposition) (p = 0.025) scores. Stroke severity in patients with MTHFRA1298C mutation was significantly increased when applying National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) (p = 0.006) and modified Rankin scale (mRS) (p = 0.020) scores. The presence of A1298C mutation as a dependent variable was associated with significantly higher TGL values (odds ratio (OR) = 2.983, 95%CI = (1.972, 7.994)).
Conclusions: The results obtained in this study demonstrate that MTHFR gene polymorphisms have a high prevalence in an NVAF cardioembolic stroke population. Moreover, an association between C677T mutation and stroke severity was highlighted. The C677T mutation in patients with NVAF was correlated with a higher incidence of cardiovascular comorbidities (hypertension HTN, heart failure (HF), dyslipidemia, type II diabetes mellitus (T2DM) with high HbA1c and increased inflammatory state). The A1298CMTHFR gene mutation was associated with a higher incidence of previous lacunar stroke and stroke recurrence rate, while dyslipidemia was the main cardiovascular comorbidity in this category.
Keywords: A1298C mutation; C677T mutation; MTHFR gene polymorphisms; cardioembolic stroke; non-valvular atrial fibrillation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
MTHFR Gene Polymorphisms and Cardiovascular Risk Factors, Clinical-Imagistic Features and Outcome in Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis.Brain Sci. 2020 Dec 27;11(1):23. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11010023. Brain Sci. 2020. PMID: 33375456 Free PMC article.
-
C677T and A1298C methylenetetrahydropholate reductase (MTHFR) polymorphisms as factors involved in ischemic stroke.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2011;52(4):1203-7. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2011. PMID: 22203923
-
Joint associations of folate, homocysteine and MTHFR, MTR and MTRR gene polymorphisms with dyslipidemia in a Chinese hypertensive population: a cross-sectional study.Lipids Health Dis. 2015 Sep 4;14:101. doi: 10.1186/s12944-015-0099-x. Lipids Health Dis. 2015. PMID: 26337056 Free PMC article.
-
Association of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T and A1298C polymorphisms with genetic susceptibility to polycystic ovary syndrome: A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis.Gene. 2019 Nov 30;719:144079. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.144079. Epub 2019 Aug 24. Gene. 2019. PMID: 31454542 Review.
-
Association of MTHFR C677T and A1298C Polymorphisms with Glaucoma Risk: a Systematic Review Meta-Analysis based 42 Case-Control Studies.Rom J Ophthalmol. 2019 Apr-Jun;63(2):107-118. Rom J Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31334388 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Impact of Thrombophilic Polymorphisms in Antenatal Women on Perinatal Health: A Single-Center Prospective Study.J Pers Med. 2024 Apr 19;14(4):433. doi: 10.3390/jpm14040433. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38673060 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between MTHFR C677T, homocysteine, and ischemic stroke in a large sample of the Han Chinese population.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Sep 23;101(38):e30562. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030562. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36197177 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Galectin-3 and Aldosterone for Predicting Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence after Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation.Cardiovasc Ther. 2022 May 23;2022:6993904. doi: 10.1155/2022/6993904. eCollection 2022. Cardiovasc Ther. 2022. PMID: 35692374 Free PMC article.
-
MTHFR Gene Polymorphisms and Cardiovascular Risk Factors, Clinical-Imagistic Features and Outcome in Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis.Brain Sci. 2020 Dec 27;11(1):23. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11010023. Brain Sci. 2020. PMID: 33375456 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of NOTCH3 p.R544C and Thrombophilia Genes in Vietnamese Patients With Ischemic Stroke: Study Involving a Hierarchical Cluster Analysis.JMIR Bioinform Biotechnol. 2024 May 7;5:e56884. doi: 10.2196/56884. JMIR Bioinform Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38935968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yiin G.S.C., Howard D.P.J., Paul N.L.M., Li L., Luengo-Fernandez R., Bull L.M., Welch S.J.V., Gutnikov S.A., Mehta Z., Rothwell P.M. Age-specific incidence, outcome, cost, and projected future burden of atrial fibrillation related embolic vascular events. Circulation. 2014;130:1236–1244. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.010942. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Le T.Q.H., Nguyen V.T., Nguyen T.K., Phan H.T. 1162: Echocardiography and cardioembolic stroke. Ultrasound Med. Boil. 2009;35:S143. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2009.06.545. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

