Autologous Mesenchymal Stem Cell Treatment is Consistently Effective for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: The Results of a Systematic Review of Treatment and Comparison to a Placebo Group
- PMID: 32722216
- PMCID: PMC7459966
- DOI: 10.3390/medicines7080042
Autologous Mesenchymal Stem Cell Treatment is Consistently Effective for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: The Results of a Systematic Review of Treatment and Comparison to a Placebo Group
Abstract
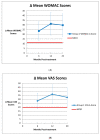
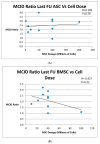
Background: Numerous studies have used autologous mesenchymal stem cell injections (AMSCI) to treat osteoarthritis. We hypothesized that AMSCI is an effective osteoarthritis treatment with increasing efficacy at higher doses. Methods: We conducted a PubMed search for human clinical studies using AMSCI for the treatment of osteoarthritis (OA) and a second search for placebo arms of injectate OA treatment. Inclusion criteria included treatment outcomes ratings both pre-treatment and at least 6 months post-treatment. Results: 45 AMSCI cohorts from 34 studies met criteria. All AMSCI cohorts showed improvement at mean 15.3 months post-treatment. Mean WOMAC and VAS scores improved at 6-months and at final follow-up (p < 0.0001 for all). Scores > 2 years were also significant (WOMAC p = 0.001/VAS p = 0.004). Results greatly exceeded the minimal clinically important difference (MCID) at each time point. AMSCI improvement also substantially exceeded previously published 6-month placebo-treatment improvement. No dose-response relationship was seen. AMSCI cohorts showed continuing improvement ≥ 6 months, and continued upward at one year. Placebo scores were already trending downward by 6 months. Conclusions: AMSCI is a consistently significantly effective treatment for osteoarthritis. It should no longer be stated that data is insufficient to establish AMSCI efficacy for OA. Given its excellent safety profile, AMSCI should be widely used for the treatment of osteoarthritis.
Keywords: adipose tissue; autologous; bone marrow aspirate; knee osteoarthritis; mesenchymal stem cell; stem cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Cross M., Smith E., Hoy D., Nolte S., Ackerman I., Fransen M., Bridgett L., Williams S., Guillemin F., Hill C.L., et al. The global burden of hip and knee osteoarthritis: Estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014;73:1323–1330. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204763. - DOI - PubMed
-
- McAlindon T.E., LaValley M.P., Harvey W.F., Price L.L., Driban J.B., Zhang M., Ward R.J. Effect of Intra-articular Triamcinolone vs Saline on Knee Cartilage Volume and Pain in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2017;317:1967–1975. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.5283. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

