Gut Microbiome Modulation for Preventing and Treating Pediatric Food Allergies
- PMID: 32722378
- PMCID: PMC7432728
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21155275
Gut Microbiome Modulation for Preventing and Treating Pediatric Food Allergies
Abstract
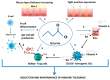
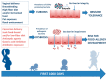
The increasing prevalence and severity of pediatric food allergies (FA) demands innovative preventive and therapeutic strategies. Emerging evidence suggests a pivotal role for the gut microbiome in modulating susceptibility to FA. Studies have demonstrated that alteration of gut microbiome could precede FA, and that particular microbial community structures early in life could influence also the disease course. The identification of gut microbiome features in pediatric FA patients is driving new prevention and treatment approaches. This review is focused on the potential role of the gut microbiome as a target for FA prevention and treatment.
Keywords: dysbiosis; food allergy; gut microbiome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hanski I., von Hertzen L., Fyhrquist N., Koskinen K., Torppa K., Laatikainen T., Karisola P., Auvinen P., Paulin L., Mäkelä M.J., et al. Environmental biodiversity, human microbiota, and allergy are interrelated. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2012;109:8334–8339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1205624109. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

