Early treatment with anti-tumor necrosis factor agents improves long-term effectiveness in symptomatic stricturing Crohn's disease
- PMID: 32723069
- PMCID: PMC7724538
- DOI: 10.1177/2050640620947579
Early treatment with anti-tumor necrosis factor agents improves long-term effectiveness in symptomatic stricturing Crohn's disease
Abstract
Background: There is limited evidence on the effectiveness of biological therapy in stricturing complications in patients with Crohn's disease.
Aim: The study aims to determine the effectiveness of anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) agents in Crohn's disease complicated with symptomatic strictures.
Methods: In this multicentric and retrospective study, we included adult patients with symptomatic stricturing Crohn's disease receiving their first anti-TNF therapy, with no previous history of biological, endoscopic or surgical therapy. The effectiveness of the anti-TNF agent was defined as a composite outcome combining steroid-free drug persistence with no use of new biologics or immunomodulators, hospital admission, surgery or endoscopic therapy during follow-up.
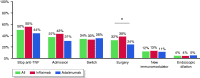
Results: Overall, 262 patients with Crohn's disease were included (53% male; median disease duration, 35 months, 15% active smokers), who received either infliximab (N = 141, 54%) or adalimumab (N = 121, 46%). The treatment was effective in 87% and 73% of patients after 6 and 12 months, respectively, and continued to be effective in 26% after a median follow-up of 40 months (IQR, 19-85). Nonetheless, 15% and 21% of individuals required surgery after 1 and 2 years, respectively, with an overall surgery rate of 32%. Postoperative complications were identified in 15% of patients, with surgical site infection as the most common. Starting anti-TNF therapy in the first 18 months after the diagnosis of Crohn's disease or the identification of stricturing complications was associated with a higher effectiveness (HR 1.62, 95% CI 1.18-2.22; and HR 1.55, 95% CI 1.1-2.23; respectively). Younger age, lower albumin levels, strictures located in the descending colon, concomitant aminosalicylates use or presence of lymphadenopathy were associated with lower effectiveness.
Conclusions: Anti-TNF agents are effective in approximately a quarter of patients with Crohn's disease and symptomatic intestinal strictures, and 68% of patients are free of surgery after a median of 40 months of follow-up. Early treatment and some potential predictors of response were associated with treatment success in this setting.
Keywords: Anti-TNF; Crohn’s disease; biologic drug; stricture; surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: IR-L has received financial support for travelling and educational activities from or has served as an advisory board member for MSD, Pfizer, Abbvie, Takeda, Janssen, Tillotts Pharma, Shire Pharmaceuticals, Ferring, Dr. Falk Pharma and Otsuka Pharmaceutical.
AP-G: has received financial support for travelling and educational activities from Rovi.
RF-I has served as a speaker for or has received research funding from Takeda, MSD, Abbvie, Janssen, Palex, Shire Pharmaceuticals, Tillotts Pharma and Casen Recordati.
MJC has received education funding from Pfizer, Janssen, MSD, Takeda, Ferring and Abbvie.
MC has served as a speaker or has received research or education funding from MSD, Abbvie, Hospira, Pfizer, Takeda, Janssen, Ferring, Shire Pharmaceuticals, Dr. Falk Pharma, and Tillotts Pharma.
JPG has served as a speaker, consultant or advisory board member for or has received research funding from MSD, Abbvie, Hospira, Pfizer, Kern Pharma, Biogen, Takeda, Janssen, Roche, Sandoz, Celgene, Ferring, Faes Farma, Shire Pharmaceuticals, Dr. Falk Pharma, Tillotts Pharma, Chiesi, Casen Fleet, Gebro Pharma, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, and Vifor Pharma.
The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest related to this manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Torres J, Mehandru S, Colombel JF, et al. Crohn's disease. Lancet 2016; 389: 1741–1755. - PubMed
-
- Friedman SL, Sheppard D, Duffield JS, et al. Therapy for fibrotic diseases: Nearing the starting line. Sci Transl Med 2013; 5: 167sr161. - PubMed
-
- Burisch J, Kiudelis G, Kupcinskas L, et al. Natural disease course of Crohn's disease during the first 5 years after diagnosis in a European population-based inception cohort: An Epi-IBD study. Gut 2019; 68(3): 423–433. - PubMed

