Artificial Intelligence in Health Care: Bibliometric Analysis
- PMID: 32723713
- PMCID: PMC7424481
- DOI: 10.2196/18228
Artificial Intelligence in Health Care: Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
Background: As a critical driving power to promote health care, the health care-related artificial intelligence (AI) literature is growing rapidly.
Objective: The purpose of this analysis is to provide a dynamic and longitudinal bibliometric analysis of health care-related AI publications.
Methods: The Web of Science (Clarivate PLC) was searched to retrieve all existing and highly cited AI-related health care research papers published in English up to December 2019. Based on bibliometric indicators, a search strategy was developed to screen the title for eligibility, using the abstract and full text where needed. The growth rate of publications, characteristics of research activities, publication patterns, and research hotspot tendencies were computed using the HistCite software.
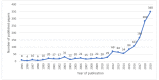
Results: The search identified 5235 hits, of which 1473 publications were included in the analyses. Publication output increased an average of 17.02% per year since 1995, but the growth rate of research papers significantly increased to 45.15% from 2014 to 2019. The major health problems studied in AI research are cancer, depression, Alzheimer disease, heart failure, and diabetes. Artificial neural networks, support vector machines, and convolutional neural networks have the highest impact on health care. Nucleosides, convolutional neural networks, and tumor markers have remained research hotspots through 2019.
Conclusions: This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the AI-related research conducted in the field of health care, which helps researchers, policy makers, and practitioners better understand the development of health care-related AI research and possible practice implications. Future AI research should be dedicated to filling in the gaps between AI health care research and clinical applications.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; bibliometric analysis; health care; machine learning; neural networks; telehealth.
©Yuqi Guo, Zhichao Hao, Shichong Zhao, Jiaqi Gong, Fan Yang. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (http://www.jmir.org), 29.07.2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Kermany DS, Goldbaum M, Cai W, Valentim CC, Liang H, Baxter SL, McKeown A, Yang G, Wu X, Yan F, Dong J, Prasadha MK, Pei J, Ting MY, Zhu J, Li C, Hewett S, Dong J, Ziyar I, Shi A, Zhang R, Zheng L, Hou R, Shi W, Fu X, Duan Y, Huu VA, Wen C, Zhang ED, Zhang CL, Li O, Wang X, Singer MA, Sun X, Xu J, Tafreshi A, Lewis MA, Xia H, Zhang K. Identifying Medical Diagnoses and Treatable Diseases by Image-Based Deep Learning. Cell. 2018 Feb 22;172(5):1122–1131.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.010. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0092-8674(18)30154-5 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lomazzo J. Fintech's Impact on Wealth Management. Ivey Business School. 2016. [2020-06-22]. https://www.ivey.uwo.ca/cmsmedia/3775893/ifp-presentation-for-scotia-dig....
-
- McFarland M. Google's artificial intelligence breakthrough may have a huge impact on self-driving cars and much more. Washington Post. [2020-02-15]. https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/innovations/wp/2015/02/25/googles-ar...
-
- Koh H, Tan G. Data mining applications in healthcare. J Healthc Inf Manag. 2005;19(2):64–72. - PubMed
-
- Wimmer H, Yoon VY, Sugumaran V. A multi-agent system to support evidence based medicine and clinical decision making via data sharing and data privacy. Decision Support Systems. 2016 Aug;88:51–66. doi: 10.1016/j.dss.2016.05.008. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials