FEDS: a Novel Fluorescence-Based High-Throughput Method for Measuring DNA Supercoiling In Vivo
- PMID: 32723920
- PMCID: PMC7387798
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.01053-20
FEDS: a Novel Fluorescence-Based High-Throughput Method for Measuring DNA Supercoiling In Vivo
Erratum in
-
Correction for Duprey and Groisman, "FEDS: a Novel Fluorescence-Based High-Throughput Method for Measuring DNA Supercoiling In Vivo".mBio. 2024 Jan 16;15(1):e0268423. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02684-23. Epub 2023 Dec 7. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38059645 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
DNA supercoiling (DS) is essential for life because it controls critical processes, including transcription, replication, and recombination. Current methods to measure DNA supercoiling in vivo are laborious and unable to examine single cells. Here, we report a method for high-throughput measurement of bacterial DNA supercoiling in vivo
Keywords: DNA gyrase; DNA topology; feedback loop; gene transcription.
Copyright © 2020 Duprey and Groisman.
Figures

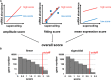
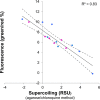
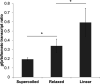

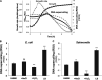
References
-
- Higgins NP. 2017. Measuring in vivo supercoil dynamics and transcription elongation rates in bacterial chromosomes, p 17–27. In The bacterial nucleoid. Humana Press, New York, NY. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
