Long Non-Coding RNA Nuclear Paraspeckle Assembly Transcript 1 (NEAT1)Relieves Sepsis-Induced Kidney Injury and Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Inflammation in HK-2 Cells
- PMID: 32724027
- PMCID: PMC7414528
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.921906
Long Non-Coding RNA Nuclear Paraspeckle Assembly Transcript 1 (NEAT1)Relieves Sepsis-Induced Kidney Injury and Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Inflammation in HK-2 Cells
Abstract
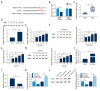
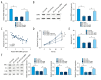
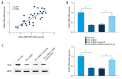
BACKGROUND Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play key roles in the development and progression of diseases, including sepsis. Therefore, this study aimed to clarify the role and underlying molecular mechanisms of lncRNA NEAT1 in sepsis. MATERIAL AND METHODS We used real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) to analyze the expression of lncRNA nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1), let-7b-5p, and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6). Western blot assay was used to measure the protein expression levels. After treatment with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), the biological behaviors of human renal tubular epithelial cells (HK-2), such as proliferation and apoptosis, were determined using 3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazol-3-ium bromide (MTT) and flow cytometry assays, respectively. The interaction relationship among NEAT1, TRAF6, and let-7b-5p was analyzed by the bioinformatics starBase database and dual-luciferase reporter assay. RESULTS lncRNA NEAT1 was expressed at higher levels in kidney tissues from sepsis patients than in healthy kidney tissues. Interestingly, LPS induced high expression of lncRNA NEAT1 in HK-2 cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, silencing of NEAT1 weakened LPS-induced apoptosis, inflammation, and inhibition of proliferation, which was overturned by silencing of let-7b-5p. In addition, overexpression of TRAF6 abolished the overexpression of let-7b-5p-induced effects on apoptosis, inflammation, and growth of HK-2 cells exposed to LPS. In summary, NEAT1 regulated TRAF6 expression by sponging let-7b-5p in HK-2 cells, which promotes LPS-induced injury and inflammation in HK-2 cells. CONCLUSIONS Our data show that the lower expression of NEAT1 impeded sepsis development and LPS-induced injury inflammation by targeting let-7b-5p/TRAF6 axis, and NEAT1 may be a target for treatment of sepsis patients.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes lipopolysaccharide-induced injury in human tubule epithelial cells by regulating miR-93-5p/TXNIP axis.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2021 Jun;210(2-3):121-132. doi: 10.1007/s00430-021-00705-6. Epub 2021 Apr 22. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33885954
-
LncRNA NEAT1 knockdown ameliorates LPS-induced human kidney injury by mediating the miR-330-5p/FOXO3 axis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2022 Oct;54(10):2683-2694. doi: 10.1007/s11255-022-03179-4. Epub 2022 Apr 1. Int Urol Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35364751
-
Circ_0001714 knockdown alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis and inflammation in renal tubular epithelial cells via miR-129-5p/TRAF6 axis in septic acute kidney injury.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2023 Aug;55(4):289-300. doi: 10.1007/s10863-023-09975-6. Epub 2023 Aug 1. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2023. PMID: 37526815
-
An updated review of contribution of long noncoding RNA-NEAT1 to the progression of human cancers.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 May;245:154380. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154380. Epub 2023 Feb 24. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37043964 Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Tumorgenesis and Metastasis of Long Non-coding RNA (lncRNA) NEAT1 in Human Solid Tumors; An Update.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Jun;82(2):593-607. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01287-9. Epub 2024 May 15. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 38750383 Review.
Cited by
-
Neat1 promotes acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease by facilitating tubular epithelial cells apoptosis via sequestering miR-129-5p.Mol Ther. 2022 Oct 5;30(10):3313-3332. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.05.019. Epub 2022 May 26. Mol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35619557 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role of LncRNA in sepsis-associated acute kidney injury.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 27;16:1627253. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1627253. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40657645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-Coding RNAs in Kidney Diseases: The Long and Short of Them.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 4;22(11):6077. doi: 10.3390/ijms22116077. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34199920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroLet-7b Regulates Neutrophil Function and Dampens Neutrophilic Inflammation by Suppressing the Canonical TLR4/NF-κB Pathway.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 29;12:653344. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.653344. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33868293 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of lncRNA MALAT1 ameliorates acute kidney injury by mediating the miR-204/APOL1 pathway.J Clin Lab Anal. 2021 Aug;35(8):e23881. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23881. Epub 2021 Jul 9. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021. PMID: 34240756 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sheng X, Zuo X, Liu X, et al. Crosstalk between TLR4 and Notch1 signaling in the IgA nephropathy during inflammatory response. Int Urol Nephrol. 2018;50:779–85. - PubMed
-
- Huang W, Lan X, Li X, et al. Long non-coding RNA PVT1 promote LPS-induced septic acute kidney injury by regulating TNFα and JNK/NF-κB pathways in HK-2 cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;47:134–40. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

