Successful recovery of recurrence of positive SARS-CoV-2 RNA in COVID-19 patient with systemic lupus erythematosus: a case report and review
- PMID: 32725351
- PMCID: PMC7385201
- DOI: 10.1007/s10067-020-05230-0
Successful recovery of recurrence of positive SARS-CoV-2 RNA in COVID-19 patient with systemic lupus erythematosus: a case report and review
Abstract
COVID-19 has become a global concern. A large number of reports have explained the clinical characteristics and treatment strategies of COVID-19, but the characteristics and treatment of COVID-19 patient with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are still unclear. Here, we report the clinical features and treatment of the first SLE patient with confirmed COVID-19 pneumonia. This was a 39-year-old woman, diagnosed with SLE 15 years ago, whose overall clinical characteristics (symptoms, laboratory tests, and chest CTs) were similar to those of the general COVID-19 patients. She continued to take the previous SLE drugs (doses of glucocorticoids, hydroxychloroquine, and immunosuppressive agents were not reduced) and was treated with strict antiviral and infection prevention treatment. After the first discharge, she got a recurrence of COVID-19 during her home isolation, and then returned to hospital and continued the previous therapy. Finally, this long-term immune suppressive patient's COVID-19 was successfully cured. The successful recovery of this case has significant reference value for the future treatment of COVID-19 patients with SLE. Key Points • COVID-19 patients with SLE is advocated to continue the medical treatment for SLE. • Hydroxychloroquine may have potential benefits for COVID-19 patients with SLE. • COVID-19 patients with SLE is prone to relapse, and multiple follow-ups are necessary.
Keywords: COVID-19; Recurrence; SARS-CoV-2; Systemic lupus erythematosus.
Figures
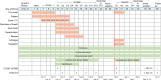
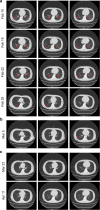
Comment in
-
COVID-19 reinfection or relapse: an intriguing dilemma.Clin Rheumatol. 2020 Nov;39(11):3189. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-05427-3. Epub 2020 Sep 26. Clin Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32980985 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in autoimmune and inflammatory conditions: clinical characteristics of poor outcomes.Rheumatol Int. 2020 Oct;40(10):1593-1598. doi: 10.1007/s00296-020-04676-4. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Rheumatol Int. 2020. PMID: 32794113 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical course, severity and mortality in a cohort of patients with COVID-19 with rheumatic diseases.Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Dec;79(12):1659-1661. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218054. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020. PMID: 32606046 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Active tuberculosis, sequelae and COVID-19 co-infection: first cohort of 49 cases.Eur Respir J. 2020 Jul 9;56(1):2001398. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01398-2020. Print 2020 Jul. Eur Respir J. 2020. PMID: 32457198 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 in Children: Clinical Approach and Management.Indian J Pediatr. 2020 Jun;87(6):433-442. doi: 10.1007/s12098-020-03292-1. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Indian J Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32338347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A complex COVID-19 case with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tocilizumab.Clin Rheumatol. 2020 Sep;39(9):2797-2802. doi: 10.1007/s10067-020-05234-w. Epub 2020 Jun 19. Clin Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32562070 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 reinfection: "New baseline" imaging concept in the era of COVID-19.Clin Imaging. 2021 Oct;78:142-145. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2021.03.021. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Clin Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33813316 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 misinformation: Mere harmless delusions or much more? A knowledge and attitude cross-sectional study among the general public residing in Jordan.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 3;15(12):e0243264. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243264. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33270783 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrence of COVID-19 after recovery ? A case series in health care workers, France.Microbes Infect. 2021 May-Jun;23(4-5):104803. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2021.104803. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Microbes Infect. 2021. PMID: 33667643 Free PMC article.
-
Is recurrence possible in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)? Case series and systematic review of literature.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021 Jan;40(1):1-12. doi: 10.1007/s10096-020-04057-6. Epub 2020 Oct 10. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33037944 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Reinfection in COVID-19 Patients in the World: A Narrative Review.Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2021 Nov 1;35:144. doi: 10.47176/mjiri.35.144. eCollection 2021. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2021. PMID: 35321379 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- COVID-19 cases worldwide. Available from: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/. Accessed 30 Apr 2020
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

