Small molecule-driven SIRT3-autophagy-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition ameliorates inflammatory crosstalk between macrophages and adipocytes
- PMID: 32726464
- PMCID: PMC7520450
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.15215
Small molecule-driven SIRT3-autophagy-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition ameliorates inflammatory crosstalk between macrophages and adipocytes
Abstract
Background and purpose: IL-1β produced by macrophages via the NOD-, LRR- and pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome, mediates the inflammatory crosstalk between macrophages and adipocytes. In our previous study, (16S,20S,24R)-12β-acetoxy-16,23-epoxy-24,25-dihydroxy-3β-(β-D-xylopyranosyloxy)-9,19-cyclolanost-22(23)-ene (AEDC), a cycloartane triterpenoid isolated from Actaea vaginata (Ranunculaceae), was found to possess anti-inflammatory effect on LPS-treated RAW264.7 macrophages. This study was designed to investigate whether AEDC modulates macrophage-adipocyte crosstalk to alleviate adipose tissue inflammation.
Experimental approach: The anti-inflammatory effect of AEDC was evaluated on LPS plus ATP-induced THP-1 macrophages and C57BL/6J mice. The expression of autophagy-related and NLRP3 inflammasome complex proteins was analysed by western blots, immunofluorescence staining and co-immunoprecipitation. The pro-inflammatory cytokines levels were determined by ELISA kits. The adipose tissue inflammation was evaluated by histological analysis and immunohistochemical staining.
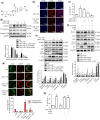
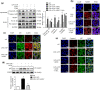
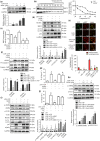
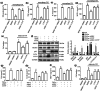
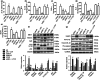
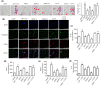
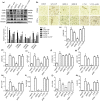
Key results: AEDC (5 and 10 μM) activated autophagy, which in turn suppressed the NLRP3 inflammasome activation and IL-1β secretion in THP-1 macrophages. AEDC increased the expression of SIRT3 deacetylase and enhanced its deacetylating activity to reverse mitochondrial dysfunction and activate AMP-activated protein kinase, which together induced autophagy. Moreover, AEDC (10 μM) attenuated macrophage conditioned medium-induced inflammatory responses in adipocytes and blocked THP-1 macrophages migration towards 3T3-L1 adipocytes. In inflammation mice, AEDC (5 and 20 mg·kg-1 ) treatment reduced the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in serum and epididymal adipose tissue and reduced macrophage infiltration to alleviate adipose tissue inflammation.
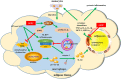
Conclusion and implications: AEDC attenuated the inflammatory crosstalk between macrophages and adipocytes through SIRT3-autophagy-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition, which might used for the treatment of adipose tissue inflammation-related metabolic disorders.
Keywords: IL-1β, macrophages; NLRP3 inflammasome; adipocytes; adipose tissue inflammation; autophagy; cycloartane triterpenoid.
© 2020 The British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Alexander, S. P. H. , Kelly, E. , Mathie, A. , Peters, J. A. , Veale, E. L. , Armstrong, J. F. , … Collaborators, C. (2019). The concise guide to pharmacology 2019/20: Introduction and other protein targets. British Journal of Pharmacology, 176(Suppl 1), S1–S20. 10.1111/bph.14747 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alexander, S. P. H. , Roberts, R. E. , Broughton, B. R. S. , Sobey, C. G. , George, C. H. , Stanford, S. C. , … Ahluwalia, A. (2018). Goals and practicalities of immunoblotting and immunohistochemistry: A guide for submission to the British Journal of Pharmacology . British Journal of Pharmacology, 175, 407–411. 10.1111/bph.14112 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chacón, M. R. , Fernandez‐Real, J. , Richart, C. , Megía, A. , Gómez, J. , Miranda, M. , … Vendrell, J. (2007). Monocyte chemoattractant protein‐1 in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Relationship with insulin‐resistance and proinflammatory cytokines. Obesity, 15, 664–672. 10.1038/oby.2007.578 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

