Long-Term Prevalence of Sensory Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy for 5 Years after Adjuvant FOLFOX Chemotherapy to Treat Colorectal Cancer: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 32727095
- PMCID: PMC7465246
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9082400
Long-Term Prevalence of Sensory Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy for 5 Years after Adjuvant FOLFOX Chemotherapy to Treat Colorectal Cancer: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
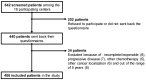
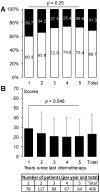
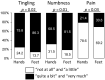
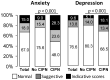
(1) Background: Oxaliplatin is among the most neurotoxic anticancer drugs. Little data are available on the long-term prevalence and consequences of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN), even though the third largest population of cancer survivors is made up of survivors of colorectal cancer. (2) Methods: A multicenter, cross-sectional study was conducted in 16 French centers to assess the prevalence of CIPN, as well as its consequences (neuropathic pain, anxiety, depression, and quality of life) in cancer survivors during the 5 years after the end of adjuvant oxaliplatin chemotherapy. (3) Results: Out of 406 patients, the prevalence of CIPN was 31.3% (95% confidence interval: 26.8-36.0). Little improvement in CIPN was found over the 5 years, and 36.5% of patients with CIPN also had neuropathic pain. CIPN was associated with anxiety, depression, and deterioration of quality of life. None of the patients with CIPN were treated with duloxetine (recommendation from American Society of Clinical Oncology), and only 3.2%, 1.6%, and 1.6% were treated with pregabalin, gabapentin, and amitriptyline, respectively. (4) Conclusions: Five years after the end of chemotherapy, a quarter of patients suffered from CIPN. The present study showed marked psychological distress and uncovered a failure in management in these patients.
Keywords: cancer survivors; colorectal cancer; health-related quality of life; oxaliplatin; peripheral neuropathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Schmoll H.J., Van Cutsem E., Stein A., Valentini V., Glimelius B., Haustermans K., Nordlinger B., van de Velde C.J., Balmana J., Regula J., et al. ESMO consensus guidelines for management of patients with colon and rectal cancer. A personalized approach to clinical decision making. Ann. Oncol. 2012;23:2479–2516. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mds236. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kerckhove N., Collin A., Condé S., Chaleteix C., Pezet D., Balayssac D. Long-term effects, pathophysiological mechanisms, and risk factors of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathies: A comprehensive literature review. Front. Pharmacol. 2017;8:86. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00086. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beijers A.J.M., Mols F., Tjan-Heijnen V.C.G., Faber C.G., van de Poll-Franse L.V., Vreugdenhil G. Peripheral neuropathy in colorectal cancer survivors: The influence of oxaliplatin administration. Results from the population-based PROFILES registry. Acta Oncol. 2015;54:463–469. doi: 10.3109/0284186X.2014.980912. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

