Estrogen receptor α phosphorylated at Ser216 confers inflammatory function to mouse microglia
- PMID: 32727504
- PMCID: PMC7390202
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-020-00578-x
Estrogen receptor α phosphorylated at Ser216 confers inflammatory function to mouse microglia
Abstract
Background: Estrogen receptor α (ERα) has been suggested to regulate anti-inflammatory signaling in brain microglia, the only resident immune cells in the brain. ERα conserves the phosphorylation motif at Ser216 within the DNA binding domain. Previously, Ser216 was found to be phosphorylated in neutrophils infiltrating into the mouse uterus and to enable ERα to regulate migration. Given the implication of this phosphorylation in immune regulation, ERα was examined in mouse microglia to determine if Ser216 is phosphorylated and regulates microglia's inflammation. It was found that Ser216 was constitutively phosphorylated in microglia and demonstrated that in the absence of phosphorylated ERα in ERα KI brains microglia inflamed, confirming that phosphorylation confers ERα with anti-inflammatory capability. ERα KI mice were obese and weakened motor ability.
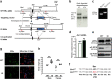
Methods: Mixed glia cells were prepared from brains of 2-days-old neonates and cultured to mature and isolate microglia. An antibody against an anti-phospho-S216 peptide of ERα (αP-S216) was used to detect phosphorylated ERα in double immunofluorescence staining with ERα antibodies and a microglia maker Iba-1 antibody. A knock-in (KI) mouse line bearing the phosphorylation-blocked ERα S216A mutation (ERα KI) was generated to examine inflammation-regulating functions of phosphorylated ERα in microglia. RT-PCR, antibody array, ELISA and FACS assays were employed to measure expressions of pro- or anti-inflammatory cytokines at their mRNA and protein levels. Rotarod tests were performed to examine motor connection ability.
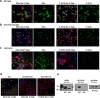
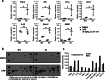
Results: Double immune staining of mixed glia cells showed that ERα is phosphorylated at Ser216 in microglia, but not astrocytes. Immunohistochemistry with an anti-Iba-1 antibody showed that microglia cells were swollen and shortened branches in the substantial nigra (SN) of ERα KI brains, indicating the spontaneous activation of microglia as observed with those of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated ERα WT brains. Pro-inflammatory cytokines were up-regulated in the brain of ERα KI brains as well as cultured microglia, whereas anti-inflammatory cytokines were down-regulated. FACS analysis showed that the number of IL-6 producing and apoptotic microglia increased in those prepared from ERα KI brains. Times of ERα KI mice on rod were shortened in Rotarod tests.
Conclusions: Blocking of Ser216 phosphorylation aggravated microglia activation and inflammation of mouse brain, thus confirming that phosphorylated ERα exerts anti-inflammatory functions. ERα KI mice enable us to further investigate the mechanism by which phosphorylated ERα regulates brain immunity and inflammation and brain diseases. Video abstract.
Keywords: Brain; Estrogen receptor; Inflammation; Microglia; Nuclear receptor; Phosphorylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


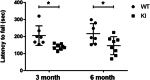
Similar articles
-
Detection and Functional Analysis of Estrogen Receptor α Phosphorylated at Serine 216 in Mouse Neutrophils.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1366:413-424. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3127-9_32. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26585153
-
Detection and Functional Analysis of Estrogen Receptor α Phosphorylated at Serine 216 in Mouse Neutrophils.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2418:63-75. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1920-9_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35119660
-
Serine 216 phosphorylation of estrogen receptor α in neutrophils: migration and infiltration into the mouse uterus.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 26;8(12):e84462. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084462. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24386386 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear receptor CAR-ERα signaling regulates the estrogen sulfotransferase gene in the liver.Sci Rep. 2020 Mar 19;10(1):5001. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-61767-9. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32193417 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Mouse Model to Analyze Non-Genomic ERα Physiological Actions.J Endocr Soc. 2022 Jul 26;6(9):bvac109. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvac109. eCollection 2022 Sep 1. J Endocr Soc. 2022. PMID: 37283844 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nuclear receptor phosphorylation in xenobiotic signal transduction.J Biol Chem. 2020 Nov 6;295(45):15210-15225. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.007933. Epub 2020 Aug 11. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32788213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Menopause to Neurodegeneration-Molecular Basis and Potential Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 11;22(16):8654. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168654. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen Receptor Alpha Splice Variants, Post-Translational Modifications, and Their Physiological Functions.Cells. 2023 Mar 14;12(6):895. doi: 10.3390/cells12060895. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36980236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Phosphotyrosine Switch in Estrogen Receptor β Is Required for Mouse Ovarian Function.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Apr 9;9:649087. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.649087. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33898441 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of female-enriched and disease-associated microglia (FDAMic) contributes to sexual dimorphism in late-onset Alzheimer's disease.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Jan 4;21(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02987-4. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 38178204 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mutoh S, Osabe M, Inoue K, Moore R, Pedersen L, Perera L, Rebolloso Y, Sueyoshi T, Negishi M. Dephosphorylation of threonine 38 is required for nuclear translocation and activation of human xenobiotic receptor CAR (NR1I3) J Biol Chem. 2009;284:34785–34792. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.048108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

