Attenuated Novel SARS Coronavirus 2 Infection in an Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Patient on Ruxolitinib
- PMID: 32727701
- PMCID: PMC7316063
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clml.2020.06.014
Attenuated Novel SARS Coronavirus 2 Infection in an Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Patient on Ruxolitinib
Abstract
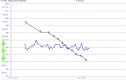
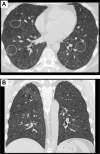
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS CoV-2) has a high death rate in patients with comorbidities or in an immunocompromised state. We report a mild and attenuated SARS CoV-2 infection in a patient who is 17 months post stem cell transplantation and maintained on the JAK/STAT inhibitor ruxolitinib, a proposed novel therapy for SARS CoV-2 pneumonia.
Keywords: Allogeneic stem cell transplantation; COVID-19; Graft-versus-host disease; Immunocompromised; JAK inhibitor.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Could ruxolitinib be effective in patients with COVID-19 infection at risk of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)?Ann Hematol. 2020 Jul;99(7):1675-1676. doi: 10.1007/s00277-020-04067-6. Epub 2020 May 14. Ann Hematol. 2020. PMID: 32405693 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Immunosuppressed Renal Transplant Recipients: A Summary of 10 Confirmed Cases in Wuhan, China.Eur Urol. 2020 Jun;77(6):748-754. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.03.039. Epub 2020 Apr 18. Eur Urol. 2020. PMID: 32317180 Free PMC article.
-
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation dilemma during the COVID-19 era.Future Oncol. 2020 Aug;16(22):1569-1573. doi: 10.2217/fon-2020-0414. Epub 2020 May 27. Future Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32458703 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Inhibition of cytokine signaling by ruxolitinib and implications for COVID-19 treatment.Clin Immunol. 2020 Sep;218:108517. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108517. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32585295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential of JAK/STAT pathway inhibition by ruxolitinib in the treatment of COVID-19.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020 Aug;54:51-62. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.06.013. Epub 2020 Jun 20. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020. PMID: 32636055 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characteristics and Outcomes of Stem Cell Transplant Patients during the COVID-19 Era: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Feb 23;12(5):530. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12050530. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38470640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 in immunocompromised patients: A systematic review of cancer, hematopoietic cell and solid organ transplant patients.J Infect. 2021 Mar;82(3):329-338. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2021.01.022. Epub 2021 Feb 4. J Infect. 2021. PMID: 33549624 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis to identify the influences of SARS-CoV-2 infections to inflammatory bowel disease.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 3;14:1024041. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1024041. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36817436 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Active, Multiorgan, Severe cGVHD After HSCT for Adolescent ALL: More Luck Than Understanding? A Case Report.Front Pediatr. 2022 Jan 14;9:775318. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.775318. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35096703 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 as a mediator of interferon deficiency and hyperinflammation: Rationale for the use of JAK1/2 inhibitors in combination with interferon.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021 Aug;60:28-45. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2021.03.006. Epub 2021 Apr 14. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021. PMID: 33992887 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

