Prognostic significance of serial molecular annotation in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and secondary acute myeloid leukemia (sAML)
- PMID: 32728186
- PMCID: PMC7854836
- DOI: 10.1038/s41375-020-0997-4
Prognostic significance of serial molecular annotation in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and secondary acute myeloid leukemia (sAML)
Abstract
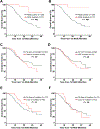
The implementation of next-generation sequencing (NGS) has influenced diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic decisions in myeloid malignancies. However, the clinical relevance of serial molecular annotation in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) undergoing active treatment is unknown. MDS or secondary acute myeloid leukemia (sAML) patients who had at least two NGS assessments were identified. Outcomes according to mutation clearance (NGS-) on serial assessment were investigated. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression models were used to evaluate the prognostic impact of NGS trajectory on overall survival (OS). A total of 157 patients (MDS [n = 95]; sAML [n = 52]; CMML [n = 10]) were identified, with 93% of patients receiving treatment between NGS assessments. Magnitude of VAF delta from baseline was significantly associated with quality of response to treatment. Patients achieving NGS- had significantly improved OS compared to patients with mutation persistence (median OS not reached vs. 18.5 months; P = 0.002), which was confirmed in multivariate analysis (HR,0.14; 95%CI = 0.03-0.56; P = 0.0064). Serial TP53 VAF evaluation predicts outcomes with TP53 clearance representing an independent covariate for superior OS (HR,0.22; 95%CI = 0.05-0.99; P = 0.048). Collectively, our study highlights the clinical value of serial NGS during treatment and warrants prospective validation of NGS negativity as a biomarker for treatment outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


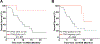
References
-
- Tefferi A, Vardiman JW. Myelodysplastic syndromes. N Engl J Med 2009. November; 361(19): 1872–1885. - PubMed
-
- Löwenberg B, Downing JR, Burnett A. Acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 1999. September; 341(14): 1051–1062. - PubMed
-
- Kayser S, Döhner K, Krauter J, Köhne CH, Horst HA, Held G, et al. The impact of therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia (AML) on outcome in 2853 adult patients with newly diagnosed AML. Blood 2011. February; 117(7): 2137–2145. - PubMed
-
- Hulegårdh E, Nilsson C, Lazarevic V, Garelius H, Antunovic P, Rangert Derolf Å, et al. Characterization and prognostic features of secondary acute myeloid leukemia in a population-based setting: A report from the Swedish Acute Leukemia Registry. American Journal of Hematology 2015; 90(3): 208–214. - PubMed
-
- Renaud L, Nibourel O, Berthon C, Roumier C, Rodriguez C, Frimat C, et al. De Novo and Secondary Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Real World Data on Outcomes from the French Nord-Pas-De-Calais Picardie Acute Myeloid Leukemia Observatory. Blood 2016; 128(22): 4013–4013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

