Radiopharmaceutical therapy in cancer: clinical advances and challenges
- PMID: 32728208
- PMCID: PMC7390460
- DOI: 10.1038/s41573-020-0073-9
Radiopharmaceutical therapy in cancer: clinical advances and challenges
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Radiopharmaceutical therapy in cancer: clinical advances and challenges.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020 Nov;19(11):819. doi: 10.1038/s41573-020-0085-5. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020. PMID: 32895501 Free PMC article.
Abstract
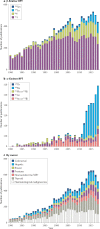
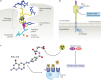
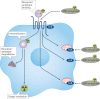
Radiopharmaceutical therapy (RPT) is emerging as a safe and effective targeted approach to treating many types of cancer. In RPT, radiation is systemically or locally delivered using pharmaceuticals that either bind preferentially to cancer cells or accumulate by physiological mechanisms. Almost all radionuclides used in RPT emit photons that can be imaged, enabling non-invasive visualization of the biodistribution of the therapeutic agent. Compared with almost all other systemic cancer treatment options, RPT has shown efficacy with minimal toxicity. With the recent FDA approval of several RPT agents, the remarkable potential of this treatment is now being recognized. This Review covers the fundamental properties, clinical development and associated challenges of RPT.
Conflict of interest statement
G.S. is a founder of and holds equity in Radiopharmaceutical Imaging and Dosimetry LLC (Rapid). He serves as a member of Rapid’s Board of Directors; this arrangement has been reviewed and approved by the Johns Hopkins University in accordance with its conflict of interest policies. M.M. was a consultant for Actinium Pharmaceuticals, Regeneron, Progenics, Bridge Medicine and General Electric. Memorial Sloan Kettering has filed for IP protection for inventions of M.M. related to alpha particle technology. L.B. was a non-paid consultant for Advanced Accelerator Applications (AAA), Ipsen, Clovis, ITM and Curium, and receives research support from AAA. Johns Hopkins University has filed for IP protection for inventions of J.N. related to alpha particle technology.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

