Index and biological spectrum of human DNase I hypersensitive sites
- PMID: 32728217
- PMCID: PMC7422677
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2559-3
Index and biological spectrum of human DNase I hypersensitive sites
Abstract
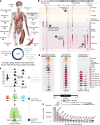
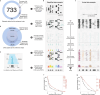
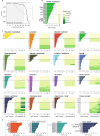
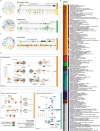
DNase I hypersensitive sites (DHSs) are generic markers of regulatory DNA1-5 and contain genetic variations associated with diseases and phenotypic traits6-8. We created high-resolution maps of DHSs from 733 human biosamples encompassing 438 cell and tissue types and states, and integrated these to delineate and numerically index approximately 3.6 million DHSs within the human genome sequence, providing a common coordinate system for regulatory DNA. Here we show that these maps highly resolve the cis-regulatory compartment of the human genome, which encodes unexpectedly diverse cell- and tissue-selective regulatory programs at very high density. These programs can be captured comprehensively by a simple vocabulary that enables the assignment to each DHS of a regulatory barcode that encapsulates its tissue manifestations, and global annotation of protein-coding and non-coding RNA genes in a manner orthogonal to gene expression. Finally, we show that sharply resolved DHSs markedly enhance the genetic association and heritability signals of diseases and traits. Rather than being confined to a small number of distal elements or promoters, we find that genetic signals converge on congruently regulated sets of DHSs that decorate entire gene bodies. Together, our results create a universal, extensible coordinate system and vocabulary for human regulatory DNA marked by DHSs, and provide a new global perspective on the architecture of human gene regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures










References
-
- Gross, D. S. & Garrard, W. T. Nuclease hypersensitive sites in chromatin. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 57, 159–197 (1988). - PubMed
-
- McGhee, J. D., Wood, W. I., Dolan, M., Engel, J. D. & Felsenfeld, G. A 200 base pair region at the 5′ end of the chicken adult β-globin gene is accessible to nuclease digestion. Cell27, 45–55 (1981). - PubMed
-
- Mills, F. C., Fisher, L. M., Kuroda, R., Ford, A. M. & Gould, H. J. DNase I hypersensitive sites in the chromatin of human μ immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes. Nature306, 809–812 (1983). - PubMed
-
- Chung, J. H., Whiteley, M. & Felsenfeld, G. A 5′ element of the chicken β-globin domain serves as an insulator in human erythroid cells and protects against position effect in Drosophila. Cell74, 505–514 (1993). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

