AAV-Mediated Combination Gene Therapy for Neuropathic Pain: GAD65, GDNF, and IL-10
- PMID: 32728596
- PMCID: PMC7378317
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtm.2020.06.018
AAV-Mediated Combination Gene Therapy for Neuropathic Pain: GAD65, GDNF, and IL-10
Abstract
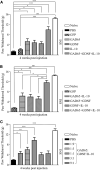
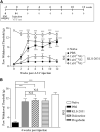
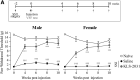
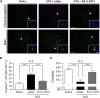
Neuropathic pain is a chronic pain state characterized by nerve damage, inflammation, and nociceptive neuron hyperactivity. As the underlying pathophysiology is complex, a more effective therapy for neuropathic pain would be one that targets multiple elements. Here, we generated recombinant adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) encoding three therapeutic genes, namely, glutamate decarboxylase 65, glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor, and interleukin-10, with various combinations. The efficacy for pain relief was evaluated in a rat spared nerve injury model of neuropathic pain. The maximal analgesic effect was achieved when the AAVs expressing all three genes were administered to rats with neuropathic pain. The combination of two virus constructs expressing the three genes was named KLS-2031 and evaluated as a potential novel therapeutic for neuropathic pain. Single transforaminal epidural injections of KLS-2031 into the intervertebral foramen to target the appropriate dorsal root ganglion produced notable long-term analgesic effects in female and male rats. Furthermore, KLS-2031 mitigated the neuroinflammation, neuronal cell death, and dorsal root ganglion hyperexcitability induced by the spared nerve injury. These results suggest that KLS-2031 represents a promising therapeutic option for refractory neuropathic pain.
Keywords: Adeno-associated virus; Gene therapy; Neuropathic pain; glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor; glutamate decarboxylase 65; interleukin-10.
© 2020 The Authors.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

