Actin cytoskeleton dynamics during mucosal inflammation: a view from broken epithelial barriers
- PMID: 32728653
- PMCID: PMC7388610
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cophys.2020.06.012
Actin cytoskeleton dynamics during mucosal inflammation: a view from broken epithelial barriers
Abstract
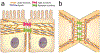
Disruption of epithelial barriers is a key pathogenic event of mucosal inflammation: It ignites the exaggerated immune response and accelerates tissue damage. Loss of barrier function is attributed to the abnormal structure and permeability of epithelial adherens junctions and tight junctions, driven by inflammatory stimuli through a variety of cellular mechanisms. This review focuses on roles of the actin cytoskeleton in mediating disruption of epithelial junctions and creation of leaky barriers in inflamed tissues. We summarize recent advances in understanding the role of cytoskeletal remodeling driven by actin filament turnover and myosin II-dependent contractility in the homeostatic regulation of epithelial barriers and barrier disruption during mucosal inflammation. We also discuss how the altered biochemical and physical environment of the inflamed tissues could affect the dynamics of the junction-associated actomyosin cytoskeleton, leading to the disruption of epithelial barriers.
Keywords: actin turnover; adherens junctions; cytoskeletal forces; non-muscle myosin II; permeability; tight junctions.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Charras G, Yap AS: Tensile Forces and Mechanotransduction at Cell-Cell Junctions. Curr Biol 2018, 28:R445–R457. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
