How do cancer cells replenish their fuel supply?
- PMID: 32729259
- PMCID: PMC7941513
- DOI: 10.1002/cnr2.1003
How do cancer cells replenish their fuel supply?
Abstract
Background: Multiple genetic changes, availability of cellular nutrients and metabolic alterations play a pivotal role in oncogenesis AIMS: We focus on cancer cell's metabolic properties, and we outline the cross talks between cellular oncogenic growth pathways in cancer metabolism. The review also provides a synopsis of the relevant cancer drugs targeting metabolic activities that are at various stages of clinical development.
Methods: We review literature published within the last decade to include select articles that have highlighted energy metabolism crucial to the development of cancer phenotypes.
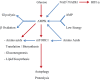
Results: Cancer cells maintain their potent metabolism and keep a balanced redox status by enhancing glycolysis and autophagy and rerouting Krebs cycle intermediates and products of β-oxydation.
Conclusions: The processes underlying cancer pathogenesis are extremely complex and remain elusive. The new field of systems biology provides a mathematical framework in which these homeostatic dysregulation principles may be examined for better understanding of cancer phenotypes. Knowledge of key players in cancer-related metabolic reprograming may pave the way for new therapeutic metabolism-targeted drugs and ultimately improve patient care.
Keywords: cancer metabolism; glutaminolysis; glycolysis; growth factors; mitochondrial transmembrane potential; systems biology.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cairns RA, Mak TW. The current state of cancer metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016;16(10):613‐614.
-
- Cairns RA, Harris IS, Mak TW. Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11(2):85‐95. - PubMed
-
- Chiarugi A, Dölle C, Felici R, Ziegler M. The NAD metabolome—a key determinant of cancer cell biology. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12(11):741‐752. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

