High plasma adiponectin is associated with increased pulmonary blood flow and reduced right ventricular function in patients with pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 32731857
- PMCID: PMC7391602
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-020-01233-4
High plasma adiponectin is associated with increased pulmonary blood flow and reduced right ventricular function in patients with pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
Background: Adiponectin is a biomarker closely related to heart failure. However, its role in pulmonary hypertension remains unclear. In this study, we investigated the association between adiponectin and hemodynamic abnormalities, right ventricular function in patients with congenital heart disease associated pulmonary hypertension (CHD-PH).
Methods: Patients with CHD-PH were enrolled in this cross-sectional study. Linear regression analysis was performed to assess the association between adiponectin, N-terminal pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide (NT-proBNP) and different clinical parameters. Results were depicted as beta-estimates(ß) with 95%-confidence intervals (95% CI). In addition, mediation and receiver operating characteristic curve analyses were used to analyze the relationships among adiponectin, NT-proBNP and right ventricular function.
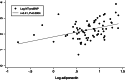
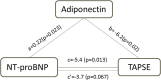
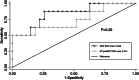
Results: A total of 86 CHD-PH patients were included. The overall mean adiponectin concentration was 7.9 ± 5.8 μg/ml. Log adiponectin was positively correlated with pulmonary circulation index (ß = 2.2, 95% CI 0.5, 4.0), log NT-proBNP (ß = 0.22, 95% CI 0.04, 0.41) and inversely with the tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE, ß = -4.7, 95% CI -8.6, - 0.8). The mediation analysis revealed the association between NT-proBNP and TAPSE was fully mediated by adiponectin (total effect c = - 5.4, 95% CI -9.4, - 1.5, p = 0.013; direct effect c' = - 3.7, 95% CI -7.5, 0.1, p = 0.067). Additionally, the efficiency of adiponectin for detecting right ventricular dysfunction was not inferior to NT-proBNP (AUC = 0.84, 95% CI 0.67-1.00 vs AUC = 0.74, 95% CI 0.51-0.97, p = 0.23).
Conclusions: Adiponectin is closely correlated with pulmonary blood flow and right ventricular function and may be a valuable biomarker for disease assessment in patients with pulmonary hypertension.
Keywords: Adiponectin; Congenital heart disease; N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide; Pulmonary hypertension; Right ventricular function.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared no conflicts of interest (including financial, political, personal, religious, ideological, academic, intellectual, commercial or any other) in relation to this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SPARCL1 and NT-proBNP as biomarkers of right ventricular-to-pulmonary artery uncoupling in pulmonary hypertension.ESC Heart Fail. 2025 Apr;12(2):1416-1426. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.15159. Epub 2024 Dec 9. ESC Heart Fail. 2025. PMID: 39654310 Free PMC article.
-
Serum N-terminal brain natriuretic peptide as a prognostic parameter in patients with pulmonary hypertension.Chest. 2006 May;129(5):1313-21. doi: 10.1378/chest.129.5.1313. Chest. 2006. PMID: 16685024
-
Plasma Growth Differentiation Factor-15 is a Potential Biomarker for Pediatric Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Associated with Congenital Heart Disease.Pediatr Cardiol. 2017 Dec;38(8):1620-1626. doi: 10.1007/s00246-017-1705-7. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Pediatr Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28819713
-
N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide as an indicator of right ventricular dysfunction.J Card Fail. 2005 Jun;11(5 Suppl):S65-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2005.04.016. J Card Fail. 2005. PMID: 15948104 Review.
-
Paediatric heart failure - understanding the pathophysiology and the current role of cardiac biomarkers in clinical practice.Cardiol Young. 2023 Apr;33(4):503-513. doi: 10.1017/S1047951123000331. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Cardiol Young. 2023. PMID: 36951045 Review.
References
-
- Diller GP, Gatzoulis MA. Pulmonary vascular disease in adults with congenital heart disease. Circulation. 2007;115(8):1039–1050. - PubMed
-
- van der Feen DE, Bartelds B, de Boer RA, Berger RMF. Assessment of reversibility in pulmonary arterial hypertension and congenital heart disease. Heart. 2019;105(4):276–282. - PubMed
-
- DeFaria YD, Stefanescu Schmidt AC, Eisman AS, Serfas JD, Naqvi M, Youniss MA, et al. Impaired right ventricular reserve predicts adverse cardiac outcomes in adults with congenital right heart disease. Heart. 2018;104(24):2044–2050. - PubMed
-
- Galie N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, Gibbs S, Lang I, Torbicki A, et al. 2015 ESC/ERS guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the joint task force for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) Eur Heart J. 2016;37(1):67–119. - PubMed
-
- Pervanidou P, Margeli A, Akalestos A, Sakka S, Kanaka-Gantenbein C, Papassotiriou I, et al. Associations between circulating N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and adiponectin concentrations depend on obesity level in female adolescents: gender dimorphic findings. Horm Metab Res. 2009;41(11):829–833. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No. U1401255/the National Nature Science Foundation of China
- 2014A050503048/the Science and Technology Department of Guangdong Province
- 2017B090904034/the Science and Technology Department of Guangdong Province
- 2017A070701013/the Science and Technology Department of Guangdong Province
- 2017030314109/the Science and Technology Department of Guangdong Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

