Hematopoietic recovery and immune reconstitution after axicabtagene ciloleucel in patients with large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 32732355
- PMCID: PMC8485681
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2020.254045
Hematopoietic recovery and immune reconstitution after axicabtagene ciloleucel in patients with large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
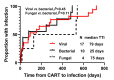
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy targeting CD19 may be associated with long-term adverse effects such as cytopenia and immune deficiency. In order to characterize these late events, we analyzed 31 patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma treated with axicabtagene ciloleucel at our institution on two clinical trials, ZUMA-1 (clinicaltrials gov. Identifier: NCT02348216) and ZUMA-9 (clinicaltrials gov. Identifier: NCT03153462). Complete blood counts, lymphocyte subsets, and immunoglobulin levels were measured serially until month 24 or progression. Fifteen (48%) patients had grade 3-4 cytopenia, including anemia (five, 16%), neutropenia (nine, 29%), or thrombocytopenia (13, 42%) at day 30. Cytopenia at day 30 was not significantly associated with later diagnosis of myelodysplasia. Among patients with ongoing remission, grade 3-4 cytopenia was observed in one of nine (11%) at 2 years. While peripheral CD8+ T cells recovered early, CD4+ T-cell recovery was delayed with a count of <200/mL in three of nine (33%) patients at 1 year and two of seven (29%) at 2 years. Immunoglobulin G levels normalized in five of nine (56%) patients at 2 years. Thirteen (42%) patients developed grade 3-4 infectious complications, including herpes zoster and Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia. These results suggest the need for prolonged monitoring and prophylaxis against opportunistic infections in these patients, to improve the longterm safety of axicabtagene ciloleucel therapy.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

