Genomic epidemiology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Santa Catarina, Southern Brazil
- PMID: 32732910
- PMCID: PMC7393130
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-69755-9
Genomic epidemiology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Santa Catarina, Southern Brazil
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Genomic epidemiology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Santa Catarina, Southern Brazil.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 2;10(1):19250. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-76386-7. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33139782 Free PMC article.
Abstract
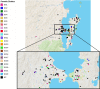
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M.tb), the pathogen responsible for tuberculosis (TB) poses as the major cause of death among infectious diseases. The knowledge about the molecular diversity of M.tb enables the implementation of more effective surveillance and control measures and, nowadays, Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) holds the potential to produce high-resolution epidemiological data in a high-throughput manner. Florianópolis, the state capital of Santa Catarina (SC) in south Brazil, shows a high TB incidence (46.0/100,000). Here we carried out a WGS-based evaluation of the M.tb strain diversity, drug-resistance and ongoing transmission in the capital metropolitan region. Resistance to isoniazid, rifampicin, streptomycin was identified respectively in 4.0% (n = 6), 2.0% (n = 3) and 1.3% (n = 2) of the 151 studied strains by WGS. Besides, resistance to pyrazinamide and ethambutol was detected in 0.7% (n = 1) and reistance to ethionamide and fluoroquinolone (FQ) in 1.3% (n = 2), while a single (0.7%) multidrug-resistant (MDR) strain was identified. SNP-based typing classified all isolates into M.tb Lineage 4, with high proportion of sublineages LAM (60.3%), T (16.4%) and Haarlem (7.9%). The average core-genome distance between isolates was 420.3 SNPs, with 43.7% of all isolates grouped across 22 genomic clusters thereby showing the presence of important ongoing TB transmission events. Most clusters were geographically distributed across the study setting which highlights the need for an urgent interruption of these large transmission chains. The data conveyed by this study shows the presence of important and uncontrolled TB transmission in the metropolitan area and provides precise data to support TB control measures in this region.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- WHO . Global Tuberculosis Report 2019. Geneva: WHO; 2019.
-
- Brasil. Ministério da Saúde. Ministério da Saúde. Departamento de Vigilância de Doenças Transmissíveis. Boletim Epidemiológico: Brasil Livre da Tuberculose: Evolução dos cenários epidemiológicos e operacionais da doença. (2019).
-
- Couvin D, David A, Zozio T, Rastogi N. Macro-geographical specificities of the prevailing tuberculosis epidemic as seen through SITVIT2, an updated version of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis genotyping database. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019;72:31–43. - PubMed
-
- van Soolingen D, et al. Molecular epidemiology of tuberculosis in The Netherlands: A nationwide study from 1993 through 1997. J. Infect. Dis. 1999;180:726–736. - PubMed
-
- Golub JE, et al. Transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis through casual contact with an infectious case. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001;161:2254–2258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

