Purine metabolism regulates DNA repair and therapy resistance in glioblastoma
- PMID: 32732914
- PMCID: PMC7393131
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-17512-x
Purine metabolism regulates DNA repair and therapy resistance in glioblastoma
Abstract
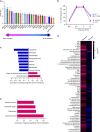
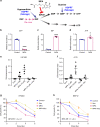
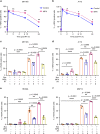
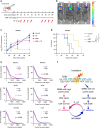
Intratumoral genomic heterogeneity in glioblastoma (GBM) is a barrier to overcoming therapy resistance. Treatments that are effective independent of genotype are urgently needed. By correlating intracellular metabolite levels with radiation resistance across dozens of genomically-distinct models of GBM, we find that purine metabolites, especially guanylates, strongly correlate with radiation resistance. Inhibiting GTP synthesis radiosensitizes GBM cells and patient-derived neurospheres by impairing DNA repair. Likewise, administration of exogenous purine nucleosides protects sensitive GBM models from radiation by promoting DNA repair. Neither modulating pyrimidine metabolism nor purine salvage has similar effects. An FDA-approved inhibitor of GTP synthesis potentiates the effects of radiation in flank and orthotopic patient-derived xenograft models of GBM. High expression of the rate-limiting enzyme of de novo GTP synthesis is associated with shorter survival in GBM patients. These findings indicate that inhibiting purine synthesis may be a promising strategy to overcome therapy resistance in this genomically heterogeneous disease.
Conflict of interest statement
D.R.W. has received research grant support from Innocrin Pharmaceuticals Inc. and Agios Pharmaceuticals Inc. for work unrelated to the content of this manuscript. The other authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 CA216449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046592/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 CA228328/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA156744/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA240515/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002240/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK097153/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99 CA241357/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK094775/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA234416/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R25 GM086262/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009676/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034933/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

