Activation and evasion of type I interferon responses by SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 32733001
- PMCID: PMC7392898
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-17665-9
Activation and evasion of type I interferon responses by SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
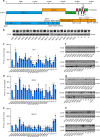
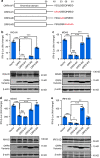
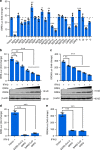
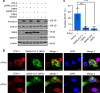
The pandemic of COVID-19 has posed an unprecedented threat to global public health. However, the interplay between the viral pathogen of COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, and host innate immunity is poorly understood. Here we show that SARS-CoV-2 induces overt but delayed type-I interferon (IFN) responses. By screening 23 viral proteins, we find that SARS-CoV-2 NSP1, NSP3, NSP12, NSP13, NSP14, ORF3, ORF6 and M protein inhibit Sendai virus-induced IFN-β promoter activation, whereas NSP2 and S protein exert opposite effects. Further analyses suggest that ORF6 inhibits both type I IFN production and downstream signaling, and that the C-terminus region of ORF6 is critical for its antagonistic effect. Finally, we find that IFN-β treatment effectively blocks SARS-CoV-2 replication. In summary, our study shows that SARS-CoV-2 perturbs host innate immune response via both its structural and nonstructural proteins, and thus provides insights into the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

