Systems Analysis of Insulin and IGF1 Receptors Networks in Breast Cancer Cells Identifies Commonalities and Divergences in Expression Patterns
- PMID: 32733384
- PMCID: PMC7359857
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00435
Systems Analysis of Insulin and IGF1 Receptors Networks in Breast Cancer Cells Identifies Commonalities and Divergences in Expression Patterns
Abstract
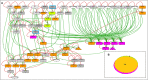
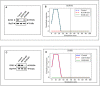
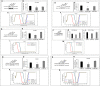
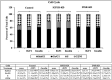
Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF1), acting respectively via the insulin (INSR) and IGF1 (IGF1R) receptors, play key developmental and metabolic roles throughout life. In addition, both signaling pathways fulfill important roles in cancer initiation and progression. The present study was aimed at identifying mechanistic differences between INSR and IGF1R using a recently developed bioinformatics tool, the Biological Network Simulator (BioNSi). This application allows to import and merge multiple pathways and interaction information from the KEGG database into a single network representation. The BioNsi network simulation tool allowed us to exploit the availability of gene expression data derived from breast cancer cell lines with specific disruptions of the INSR or IGF1R genes in order to investigate potential differences in protein expression that might be linked to biological attributes of the specific receptor networks. Modeling-generated information was corroborated by experimental and biological assays. BioNSi analyses revealed that the expression of 75 and 71 genes changed during simulation of IGF1R-KD and INSR-KD, compared to control cells, respectively. Out of 16 proteins that BioNSi analysis was based on, validated by Western blotting, nine were shown to be involved in DNA repair, eight in cell cycle checkpoints, six in proliferation, eight in apoptosis, seven in oxidative stress, six in cell migration, two in energy homeostasis, and three in senescence. Taken together, analyses identified a number of commonalities and, most importantly, dissimilarities between the IGF1R and INSR pathways that might help explain the basis for the biological differences between these networks.
Keywords: BioNSi; IGF1 receptor (IGF1R); insulin receptor (INSR); insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF1); network simulation; systems analysis.
Copyright © 2020 Sarfstein, Yeheskel, Sinai-Livne, Pasmanik-Chor and Werner.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Differential Effects of Insulin and IGF1 Receptors on ERK and AKT Subcellular Distribution in Breast Cancer Cells.Cells. 2019 Nov 23;8(12):1499. doi: 10.3390/cells8121499. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31771180 Free PMC article.
-
Both IGF1R and INSR Knockdown Exert Antitumorigenic Effects in Prostate Cancer In Vitro and In Vivo.Mol Endocrinol. 2015 Dec;29(12):1694-707. doi: 10.1210/me.2015-1073. Epub 2015 Oct 9. Mol Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 26452103 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic functions of IGF1R and INSR in prostate cancer include enhanced tumor growth, cell migration and angiogenesis.Oncotarget. 2014 May 15;5(9):2723-35. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1884. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 24809298 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Nuclear Insulin and IGF1 Receptors in Metabolism and Cancer.Biomolecules. 2021 Apr 2;11(4):531. doi: 10.3390/biom11040531. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33918477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Minireview: nuclear insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 receptors: a novel paradigm in signal transduction.Endocrinology. 2013 May;154(5):1672-9. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-2165. Epub 2013 Mar 18. Endocrinology. 2013. PMID: 23507573 Review.
Cited by
-
Hallmarks of cancer: The insulin-like growth factors perspective.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 21;12:1055589. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1055589. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36479090 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sarfstein R, Werner H. The Insulin/IGF1 receptors family. In: Wheeler DL, Yarden Y. editors, The Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Handbook. New York, NY: Springer Science; (2015). p. 297–320.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

