Validation of Droplet Digital Polymerase Chain Reaction for Salmonella spp. Quantification
- PMID: 32733415
- PMCID: PMC7358645
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01512
Validation of Droplet Digital Polymerase Chain Reaction for Salmonella spp. Quantification
Abstract
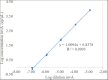
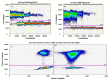
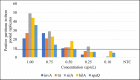
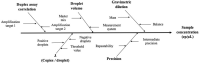
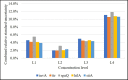
Salmonellosis is a foodborne disease caused by Salmonella spp. Although cell culture is the gold standard for its identification, validated molecular methods are becoming an alternative, because of their rapidity, selectivity, and specificity. A simplex and duplex droplet digital polymerase chain reaction (ddPCR)-based method for the identification and quantification of Salmonella using ttr, invA, hilA, spaQ, and siiA gene sequences was validated. The method has high specificity, working interval between 8 and 8,000 cp/μL in ddPCR reaction, a limit of detection of 0.5 copies/μL, and precision ranging between 5 and 10% measured as a repeatability standard deviation. The relative standard measurement uncertainty was between 2 and 12%. This tool will improve food safety in national consumption products and will increase the competitiveness in agricultural product trade.
Keywords: Salmonella; bioanalysis; droplet digital PCR; food safety; validation.
Copyright © 2020 Villamil, Calderon, Arias and Leguizamon.
Figures




References
-
- BioRad (2018). Droplet Digital PCR Applications Guide. Available online at: http://www.bio-rad.com/webroot/web/pdf/lsr/literature/Bulletin_6407.pdf (accessed April 18, 2020).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

