Comparison of the Effects of Cyclophosphamide and Mycophenolate Mofetil Treatment Against Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 32733900
- PMCID: PMC7358520
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00253
Comparison of the Effects of Cyclophosphamide and Mycophenolate Mofetil Treatment Against Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
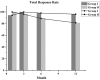
Background: Although there are multiple ways to manage immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD), including treatment with glucocorticoids, "steroid-sparing" immunosuppressive drugs, or biologic agents, few clinical trials on IgG4-RD have been conducted. This study aimed to compare the efficacy and safety of glucocorticoids (GCs) combined with cyclophosphamide (CYC) or mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) in IgG4-RD patients. This cohort study was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (ID: NCT01670695). Methods: This retrospective study included 155 IgG4-RD patients who received GCs with CYC or MMF at the Department of Rheumatology at Peking Union Medical College Hospital between January 2012 and July 2018. Propensity score matching (PSM) was conducted to match two groups of patients based on their baseline clinical characteristics. Treatment response, relapse rate, and drug safety were analyzed. The treatment response was evaluated based on complete response (CR), partial response (PR), and no change (NC), and the cumulative relapse rate and adverse events in each treatment group were compared using Kaplan-Meier curves and log-rank test, respectively. Results: Of the 155 IgG4-RD patients, 90 were treated with GCs plus CYC (group I) and 65 with GCs plus MMF (group II). After propensity score-matched (PSM) analysis, 108 patients were selected (54 in each group), 49 of whom had "definite" IgG4-RD, 8 "probable" IgG4-RD, and 51 "possible" IgG4-RD. At the last follow-up, the total response in groups I and II was 98.15 and 96.3%, respectively, and within 12 months, the cumulative relapse rate in group II was significantly higher than that in group I (14.8 vs. 3.7%, P = 0.046). Recurrence occurred at the paranasal sinus, lacrimal glands, skin, lung, pancreas, and bile ducts, and the relapsed patients achieved remission after switching immunosuppressants or/and increasing the GC dose. Conclusions: In IgG4-RD patients with internal organ involvement, GCs plus CYC or MMF are both effective with similar effects in disease response, while GCs plus CYC reduced the relapse rate better than GCs plus MMF.
Keywords: IgG4-related disease; cyclophosphamide; efficacy; mycophenolate mofetil; relapse; response.
Copyright © 2020 Luo, Peng, Zhang, Li, Liu, Lu, Zhang, Zeng, Zhang, Fei and Zhang.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparison of the efficacy and safety of leflunomide versus mycophenolate mofetil in treating IgG4-related disease: a retrospective cohort study.Clin Rheumatol. 2023 Jul;42(7):1839-1846. doi: 10.1007/s10067-023-06528-5. Epub 2023 Feb 13. Clin Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 36781683
-
Additive effect of leflunomide and glucocorticoids compared with glucocorticoids monotherapy in preventing relapse of IgG4-related disease: A randomized clinical trial.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2020 Dec;50(6):1513-1520. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2020.01.010. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2020. PMID: 32113839 Clinical Trial.
-
Addition of second-line steroid sparing immunosuppressants like mycophenolate mofetil improves outcome of Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD): a series from a tertiary care teaching hospital in South India.Rheumatol Int. 2018 Feb;38(2):203-209. doi: 10.1007/s00296-017-3730-5. Epub 2017 May 26. Rheumatol Int. 2018. PMID: 28550399
-
Glucocorticoids in the treatment of IgG4-related disease-Prospects for new international treatment guidelines.Mod Rheumatol. 2023 Mar 2;33(2):252-257. doi: 10.1093/mr/roac097. Mod Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 35993488 Review.
-
Combination therapy of leflunomide and glucocorticoids for the maintenance of remission in patients with IgG4-related disease: a retrospective study and literature review.Intern Med J. 2017 Jun;47(6):680-689. doi: 10.1111/imj.13430. Intern Med J. 2017. PMID: 28321964 Review.
Cited by
-
Improved clinical outcomes of tocilizumab versus cyclophosphamide for IgG4-related disease: insights from a prospective IgG4-related disease registry.Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2021 Jun 30;12:20406223211028776. doi: 10.1177/20406223211028776. eCollection 2021. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2021. PMID: 34262681 Free PMC article.
-
IgG4-related disease - focus on digestive system involvement.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 18;16:1584107. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1584107. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40612937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenic roles of follicular helper T cells in IgG4-related disease and implications for potential therapy.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 7;15:1413860. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1413860. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38911857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of IgG4-related cholangitis: diagnosis, therapy, and long-term surveillance.Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2025 Apr 4;13:goaf032. doi: 10.1093/gastro/goaf032. eCollection 2025. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2025. PMID: 40191403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical features of immunoglobulin G4-related spinal pachymeningitis.Front Hum Neurosci. 2025 Jul 17;19:1541096. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2025.1541096. eCollection 2025. Front Hum Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40746909 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Venetsanopoulou A, Tzioufas A. 58-year-old patient with IgG4-related thoracic aortitis. Mediterr J Rheumatol. (2016) 27:191–3. 10.31138/mjr.27.4.191 - DOI
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

