Understanding the Role of Interleukin-6 (IL-6) in the Joint and Beyond: A Comprehensive Review of IL-6 Inhibition for the Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 32734482
- PMCID: PMC7410942
- DOI: 10.1007/s40744-020-00219-2
Understanding the Role of Interleukin-6 (IL-6) in the Joint and Beyond: A Comprehensive Review of IL-6 Inhibition for the Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
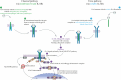
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, debilitating autoimmune disorder involving inflammation and progressive destruction of the joints, affecting up to 1% of the population. The majority of patients with RA have one or more comorbid conditions, the most common being cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, and depression, the presence of which are associated with poorer clinical outcomes and lower health-related quality of life. RA pathogenesis is driven by a complex network of proinflammatory cells and cytokines, and of these, interleukin-6 (IL-6) plays a key role in the chronic inflammation associated with RA. Through cell signaling that can be initiated by both membrane-bound and soluble forms of its receptor, IL-6 acts both locally to promote joint inflammation and destruction, and in the circulation to mediate extra-articular manifestations of RA, including pain, fatigue, morning stiffness, anemia, and weight loss. This narrative review describes the role of IL-6 in the pathogenesis of RA, its comorbidities, and extra-articular systemic manifestations, and examines the effects of the IL-6 receptor inhibitors sarilumab and tocilizumab on clinical endpoints of RA, patient-reported outcomes, and common comorbidities and extra-articular manifestations.
Keywords: Antirheumatic agents; C-reactive protein; Comorbidity; Inflammation; Interleukin-6; Rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ennio G. Favalli has received consulting fees and/or speaking engagements from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Lilly, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi Genzyme, and Union Chimique Belge.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

