Clinical characteristics, laboratory outcome characteristics, comorbidities, and complications of related COVID-19 deceased: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 32734576
- PMCID: PMC7391922
- DOI: 10.1007/s40520-020-01664-3
Clinical characteristics, laboratory outcome characteristics, comorbidities, and complications of related COVID-19 deceased: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: At present, novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has become a serious global public health problem. The current meta-analysis aimed to find risk factors for the COVID-19-related death, helping to enhance the efficacy and reduce the mortality of COVID-19.
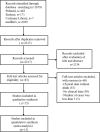
Methods: We searched PubMed, Embase, medRxiv, and Cochrane Library for articles published between January 1, 2020, and April 13, 2020. We statistically analyzed the risk factors of the COVID-19 deceased with meta-analysis.
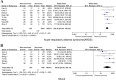
Results: A total of 2401 patients in 15 articles were included in this study. Meta-analysis showed that 66.6% of COVID-19 deceased were male, with a median age of 69.9 years. Common symptoms of deceased included fever (70.6-100%), dyspnea (38.89-85.7%), cough (22.4-78%), and fatigue (22-61.9%). The incidence of hypertension, chronic cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and chronic cerebrovascular disease among the COVID-19 deceased were 38.56% (95% confidence interval (CI) 25.84 ~ 52.12%), 17.54% (95% CI 13.38 ~ 21.69%), 22.2% (95% CI 19.30 ~ 25.10%), and 15.58% (95% CI 10.05 ~ 21.12%), respectively. Compared with the surviving COVID-19 patients, the deceased had lower platelet levels (mean difference (MD) = - 39.35, 95% CI - 55.78 ~ - 22.93) and higher C-reactive protein (CRP) (MD = 80.85, 95% CI 62.53 ~ 99.18) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) (MD = 246.65, 95% CI 157.43 ~ 335.88) at admission. The most common complications of the deceased were acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) (OR = 100.36, 95% CI 64.44 ~ 156.32) and shock (OR = 96.60, 95% CI 23.80 ~ 392.14).
Conclusion: Most of the COVID-19 deceased were elderly males. Fever, dyspnea, dry cough, fatigue, hypertension, chronic cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease, diabetes, and laboratory examinations showed low levels of platelet content, increased CRP and LDH were associated with the risk of dying. ARDS and shock were risk factors for death in COVID-19 patients.
Keywords: COVID-19; Death; Meta-analysis; Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Conflict of interest statement
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report–84 (https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio...). Accessed 13 Apr 2020
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

