Extra-abdominal manifestations of retroperitoneal infection: a case of popliteal sinus secondary to duodenal ulcer
- PMID: 32734780
- PMCID: PMC7591615
- DOI: 10.1308/rcsann.2020.0137
Extra-abdominal manifestations of retroperitoneal infection: a case of popliteal sinus secondary to duodenal ulcer
Abstract
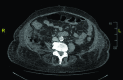
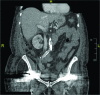
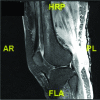
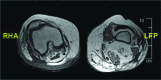
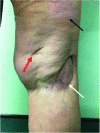
Retroperitoneal abscesses can be gastrointestinal, urological or vascular in origin, and can spread via the retrofascial compartment through the psoas muscle to the lower limb. We describe the case of a 73-year-old woman with right knee pain for three weeks, a cellulitic right thigh and cholestatic liver function tests. A purulent sinus developed in the popliteal fossa and computed tomography of the abdomen revealed a right-sided retroperitoneal collection with gas, extending to the right pelvis and inguinal region. The popliteal fossa sinus and retroperitoneal collection were identified as a single pathology through computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging and culture of identical organisms. At laparotomy, perforated duodenal ulcer disease was identified as the cause of the retroperitoneal abscess. Clinicians should seek to exclude retroperitoneal sources of infection in cases of lower leg infection, including perforated duodenal ulcer, caecal adenocarcinoma and appendicitis.
Keywords: Abdominal abscess; Duodenal ulcer surgery; Lower extremity surgery; Retroperitoneal space.
Figures
References
-
- Simons G, Sty J, Starshak R. Retroperitoneal and retrofascial abscesses: a review. J Bone Joint Surg 1983; : 1041–1058. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

