Dynamics of Cell Membrane Permeabilization by Saponins Using Terahertz Attenuated Total Reflection
- PMID: 32735777
- PMCID: PMC7451926
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2020.05.040
Dynamics of Cell Membrane Permeabilization by Saponins Using Terahertz Attenuated Total Reflection
Abstract
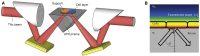
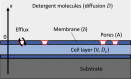
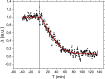
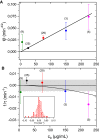
Understanding the relevant parameters of the formation of pores during permeabilization is very challenging for medical applications. Several components are involved: the arrival of the permeabilizing molecules to the membrane, the efficiency of formation of the pores and their specific dynamics, and the flux of molecules through the plasma membrane. Using attenuated total reflection in the terahertz domain, we studied the dynamics of Madine-Darby canine kidney cells after permeabilization by saponin molecules. We developed an analytical model taking into account saponin molecule diffusion, cell geometry, cytosol molecule diffusion, and pore dynamics. We also studied the effect of possible pore overlapping on the cell membrane, introducing a dimensionless quantity that is the ratio between overlapping and diffusive effects. Pores are found to be static within 1 h after their creation, hinting that the diffusion of the saponin molecules to the membrane is the limiting factor in our experiments.
Copyright © 2020 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Stewart M.P., Sharei A., Jensen K.F. In vitro and ex vivo strategies for intracellular delivery. Nature. 2016;538:183–192. - PubMed
-
- Hapala I. Breaking the barrier: methods for reversible permeabilization of cellular membranes. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 1997;17:105–122. - PubMed
-
- Eeman M., Deleu M. From biological membranes to biomimetic model membranes. Biotechnol. Agron. Soc. Environ. 2010;14:719–736.
-
- Ros U., García-Sáez A.J. More than a pore: the interplay of pore-forming proteins and lipid membranes. J. Membr. Biol. 2015;248:545–561. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

