The four horsemen of a viral Apocalypse: The pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19)
- PMID: 32736307
- PMCID: PMC7387269
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102887
The four horsemen of a viral Apocalypse: The pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19)
Abstract
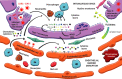
The pathogenesis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) may be envisaged as the dynamic interaction between four vicious feedback loops chained or happening at once. These are the viral loop, the hyperinflammatory loop, the non-canonical renin-angiotensin system (RAS) axis loop, and the hypercoagulation loop. Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-coronavirus (CoV)-2 lights the wick by infecting alveolar epithelial cells (AECs) and downregulating the angiotensin converting enzyme-2 (ACE2)/angiotensin (Ang-1-7)/Mas1R axis. The viral feedback loop includes evading the host's innate response, uncontrolled viral replication, and turning on a hyperactive adaptative immune response. The inflammatory loop is composed of the exuberant inflammatory response feeding back until exploding in an actual cytokine storm. Downregulation of the ACE2/Ang-(1-7)/Mas1R axis leaves the lung without a critical defense mechanism and turns the scale to the inflammatory side of the RAS. The coagulation loop is a hypercoagulable state caused by the interplay between inflammation and coagulation in an endless feedback loop. The result is a hyperinflammatory and hypercoagulable state producing acute immune-mediated lung injury and eventually, adult respiratory distress syndrome.
Keywords: ACE2; Acute lung injury; Adult distress respiratory syndrome; COVID-19; Hypercoagulability; Hyperinflammatory state; RAS; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest We declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- WHO. Novel coronavirus – China. Jan 12, 2020. http://www.who.int/csr/don/12-january-2020-novel-coronavirus-china/en/ (accessed May 20, 2020).
-
- Johns Hopkins. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

