Neuromodulation of brain activation associated with addiction: A review of real-time fMRI neurofeedback studies
- PMID: 32736324
- PMCID: PMC7394772
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102350
Neuromodulation of brain activation associated with addiction: A review of real-time fMRI neurofeedback studies
Abstract
Real-time functional magnetic resonance imaging neurofeedback (rtfMRI-nf) has emerged in recent years as an imaging modality used to examine volitional control over targeted brain activity. rtfMRI-nf has also been applied clinically as a way to train individuals to self-regulate areas of the brain, or circuitry, involved in various disorders. One such application of rtfMRI-nf has been in the domain of addictive behaviors, including substance use. Given the pervasiveness of substance use and the challenges of existing treatments to sustain abstinence, rtfMRI-nf has been identified as a promising treatment tool. rtfMRI-nf has also been used in basic science research in order to test the ability to modulate brain function involved in addiction. This review focuses first on providing an overview of recent rtfMRI-nf studies in substance-using populations, specifically nicotine, alcohol, and cocaine users, aimed at reducing craving-related brain activation. Next, rtfMRI-nf studies targeting reward responsivity and emotion regulation in healthy samples are reviewed in order to examine the extent to which areas of the brain involved in addiction can be self-regulated using neurofeedback. We propose that future rtfMRI-nf studies could be strengthened by improvements to study design, sample selection, and more robust strategies in the development and assessment of rtfMRI-nf as a clinical treatment. Recommendations for ways to accomplish these improvements are provided. rtfMRI-nf holds much promise as an imaging modality that can directly target key brain regions involved in addiction, however additional studies are needed in order to establish rtfMRI-nf as an effective, and practical, treatment for addiction.
Keywords: Addiction; Emotion; Neurofeedback; Reward; real-time fMRI.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
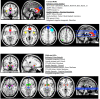
Figures
Similar articles
-
Self-regulation of human brain activity using simultaneous real-time fMRI and EEG neurofeedback.Neuroimage. 2014 Jan 15;85 Pt 3:985-95. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.04.126. Epub 2013 May 11. Neuroimage. 2014. PMID: 23668969
-
Cigarette craving modulation is more feasible than resistance modulation for heavy cigarette smokers: empirical evidence from functional MRI data.Neuroreport. 2021 Jun 9;32(9):762-770. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000001653. Neuroreport. 2021. PMID: 33901056
-
Mediation analysis of triple networks revealed functional feature of mindfulness from real-time fMRI neurofeedback.Neuroimage. 2019 Jul 15;195:409-432. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.03.066. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Neuroimage. 2019. PMID: 30953836 Clinical Trial.
-
Optimizing real time fMRI neurofeedback for therapeutic discovery and development.Neuroimage Clin. 2014 Jul 10;5:245-55. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2014.07.002. eCollection 2014. Neuroimage Clin. 2014. PMID: 25161891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-time functional MRI neurofeedback: a tool for psychiatry.Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2014 Sep;27(5):332-6. doi: 10.1097/YCO.0000000000000087. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 25023886 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the therapeutic potential of tDCS, TMS and DBS in overcoming tobacco use disorder: an umbrella review.AIMS Neurosci. 2024 Oct 23;11(4):449-467. doi: 10.3934/Neuroscience.2024027. eCollection 2024. AIMS Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39801797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Cognition-Guided Neurofeedback BCI Dataset on Nicotine Addiction.Front Neurosci. 2021 Jul 6;15:647844. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.647844. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34295217 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical response to neurofeedback in major depression relates to subtypes of whole-brain activation patterns during training.Mol Psychiatry. 2025 Jun;30(6):2707-2717. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02880-3. Epub 2024 Dec 26. Mol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 39725743 Free PMC article.
-
Updated Perspectives on the Neurobiology of Substance Use Disorders Using Neuroimaging.Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2023 Aug 10;14:99-111. doi: 10.2147/SAR.S362861. eCollection 2023. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2023. PMID: 37583934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computationally Informed Interventions for Targeting Compulsive Behaviors.Biol Psychiatry. 2023 Apr 15;93(8):729-738. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2022.08.028. Epub 2022 Sep 7. Biol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36464521 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allman J.M., Hakeem A., Erwin J.M., Nimchinsky E., Hof P. The anterior cingulate cortex: the evolution of an interface between emotion and cognition. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001;935:107–117. - PubMed
-
- Bush G., Luu P., Posner M.I. Cognitive and emotional influences in anterior cingulate cortex. Trends in Cognit. Sci. 2000;4(6):215–222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

